Glass roofs are a vital source of daylight, reducing the need for artificial lighting. In recent years, installation of a skylight has become one of the most common choices for home and office lighting. A skylight provides daylight, ventilation and a view of the night & day sky. When properly selected and installed, skylight can help minimize heating, cooling, and lighting costs. Before selecting skylight for a project, the type of skylight that would work best is to be determined as also its positioning to optimize contribution to building’s energy efficiency.
Post your Requirement
WFM called upon leading domain experts across various sectors of the industry to understand what they viewed as the most important factors while designing and installing roofing and skylights. We discussed a variety of topics on skylights and roofing including choice of right materials, correct installation practices, types of glazing, maintenance, safety and security, energy efficiency, and common problems in roofing and sky lights.

Dome at Amanora Town Centre, Pune

Skylight at ONGC building, Delhi
Skylights Zarokha to Skyroof emitting the glow
I pushed open the skylight and dangled my arms out in the starlight. There was another roof window half open just across the street, and even though no melancholy arms slithered out from beneath it I could see the light from within, and hear a faint musical beat beat beat…
Enquire Now for UPVC Windows
Skylights can soak a room in natural light, making it bright, cheerful and cosy, completely changing its dreariness. Skylights are literally windows in the roof, allowing you to bring a bit of blue sky into your home and display the splendour of the stars and the moon. In addition to the primary role of protection against outdoor environment, skylights help in cutting down the need for artificial light and air conditioning.
“The beam of light through a glass tile amidst other tiles in a country tile roof, would fill up the room with divine light. This small little source of light would make a room lively even on a gloomy rainy day! My childhood memories of skylights are associated with this little tile that would let in the ethereal light on a full moon night and also the first beam of sunlight in the morning like a wake-up call….”
So beautifully expressed by Dhananjay Dake, an expert in new age architectural engineering and the Creative Director, Catalysers, Pune.

Dhananjay Dake, Director,
Construction Catalyser
In a way, natural light through a roof has always been magical and adds great value to the space below. Considering the climatic conditions in India, surface area of a skylight and its location plays a vital role in creating appropriate quality of light and cross ventilation for habitable spaces. Sandeep Roy, COO, Nelson (a global architecture firm) cites that primary objective of incorporating skylights in any design is to bring natural light into the inner sanctum, which is probably difficult to reach through peripheral vertical openings.

Sandeep Roy, Chief Operating
Officer, Nelson
Skylights improve energy efficiency of a building. Harnessing solar energy with skylights to fill a space with diffused light is more efficient than using vertical windows. But if not installed properly, skylights can make a room uncomfortable through unwanted heat ingress, which make the air conditioner work harder in summer or allow precious heat to escape in winter. Skylights can let in almost four times the amount of heat as a standard window. Heat gain is to be managed effectively to optimise between air conditioning load and lighting requirements. Energy experts estimate that a 2-foot by 4-foot skylight made with a single pane of clear glass increases air conditioning load by 240 kilowatt hours per year.
Key Factors to Consider While Designing and Installing Skylight
Skylight becomes one of the important elements of a building envelope once it is conceived by an architect. Daylight brings along heat and glare, intensity of which depends on geographical location, orientation and positioning in the building. Here are few key factors to be considered while designing and installing skylights.

Arijit Ghosh, Principal Architect,
Studio 4th Dimension
While optimising energy efficiency is a primary requirement, an important factor in designing and installing skylights is aesthetics, i.e., the looks of the skylight from inside as well as outside, says Arijit Ghosh, Principal Architect, Studio 4th Dimension. One should consider nature of the space where light is to be drawn into as also intensity requirements.
The aesthetics of skylight is only occasionally external but almost always internal, in the sense that it renders special character to the space it covers. Most great examples of skylights we see around us are beautiful, not because they add to the skyline of the city but because they create wonderful spaces under them, points out Sandeep Roy.

Ashish K Jain, Partner,
AEON Integrated Building Design
Consultant LLP
There are two schools of structural aesthetics in skylights – one which makes for a pattern/rhythm in the structure itself and another that expects the structure to be minimal and celebrates the glass. Skylights are one of those parts of the building where true structural aesthetics could be showcased.
The key factors that influence the design of skylight include functional requirement of the building/space in question, its floor to roof height, quantum of daylight penetration, visual comfort, thermal comfort and energy efficiency, points out Ashish K Jain, Partner, AEON Integrated Building Design Consultant LLP.

Manish Banker, Founder and
Principal Architect, TAO
Architecture Pvt. Ltd
The most important aspect to consider while designing any skylight is to achieve glare free light and ventilation, says Manish Banker, Founder and Principal Architect, TAO Architecture Pvt. Ltd.

Akhila Anantharaman, Director,
Geodesic Consulting Pvt Ltd
While designing and installing skylights, one must consider the sun path in conjunction with the layout of the building, observes Akhila Anantharaman, Director, Geodesic Consulting Pvt Ltd. Sun path study takes into account the time of day, date of the year, orientation of the building, the latitude and longitude of the site, roofing and cladding materials used, usage of the building and layout of the space.
Enquire Now for Cladding & Facades
“Skylights are added to buildings mainly to increase daylighting within the building, in-turn reducing energy costs and improving comfort by using natural sources of light. But if not designed properly, the same skylights can become a burden on the energy consumption by increasing radiant heat and in-turn air conditioning loads with increased glare from direct sunlight creating unfavourable working conditions in the building,” says Akhila.
The sky-lit area requires to be weather-proof, advises Sandeep Roy, otherwise it might as well be kept open to sky. The functional objectives of skylights is therefore self-explanatory – that it has to bring in light and prevent rain or unwanted sun.

Abhishek kumar Sinha, Project
Architect, Turner Construction
Company
There are some broad aspects to be observed while designing skylights for execution, says Abhishek kumar Sinha, Project Architect, Turner Construction Company. Installation details vary with the kind of material selected for skylights. Other governing factors to decide on the right skylight is safety (with respect to fire and fall hazard), structural integrity, acoustic requirements, thermal conductance and light transmittance, says Sinha, who is also an architect associated with GRIHA (GRIHA-Evaluator) and LEED (a LEED Green Associate).

Rajan Govind, Director,
BES Consultants Pvt Ltd
Agreeing with Sinha on said safety aspects, Rajan Govind, Director & Façade Specialist, BES Consultants Pvt Ltd also notes that skylights should consider human safety and maintenance loads in addition to standard design criteria. Appropriate glass and safety compliances are primary aspects of skylight designs. Rajan Govind notes that incorrect glass specification may lead to very high cooling loads and discomfort to occupants.
The installation of skylights is typically the last activity while closing building envelope and hence requires a coordination with other trades since inception of design. The drainage of rain water and interface with wall and roof assembly are the most critical details that can create challenging aftereffects if not dealt with due diligence while detailing and installation, notes architect Sinha.
Acoustic and thermal properties of the glass used are also equally important. Heat loss through skylights is inevitable considering the convection currents set in due to hot and cold air temperature difference, explains Dhananjay Dake. Such a condition is not comfortable for cold regions; but in India, except for the northern region, skylight with vents are very effective to set in convection currents for escape of hot air and replacing with cool air.

Dome for a project at Mysore

An Office Building at Pune
Selection of Location for Skylights : The selection of location of skylights is based on the sun path study. Small changes based on this study can go a long way. For example, results from the study can be used in design to ensure that diffused light from skylights on work benches or desks. After determining the appropriate location of skylights, two main aspects are considered namely glazing material and supporting system or assembly.
How to Choose and Install Correct Skylights : Span, shape of roof opening and economics are the three prime determinants for design of skylights. In some situations, when the glass needs to be accessible and walkable above (like a glass floor), a flat skylights can be designed. In principle, such a skylight is designed simply as a horizontal curtain-wall which can take the load of whatever is happening on top of it.

IBM Food Court, Bengaluru
The design of skylight should be based on the type of building application too, says Ashish Jain of AEON. For example, skylights for an industrial building will be very different than for an atrium in a retail or commercial building.
Skylights typically are constructed with either plastic or glass, and the choice depends on several factors, including climate, location within the building and budget, states Ar. Jain. Plastic glazing for skylights is less expensive than glass glazing and yet it is fairly durable. However, plastic is more susceptible to wear and will scratch, discolour or warp easily. Unless the plastic is coated with a special film, adds Jain, this kind

Raja Bhoj International Airport, Bhopal
of glazing could let in dangerous ultraviolet (UV) rays, which could harm people and fade interior finishes too. Though glass glazing for skylights is comparatively expensive, it is generally preferred to plastic due to its durability, better looks and the fact that it doesn’t discolour over time. Glass also provides wider options to achieve the balance between daylight and energy efficiency. Therefore a glazing that can achieve a balance between day light for visual comfort, heat gains for energy efficiency and of course safety and aesthetics should be chosen.
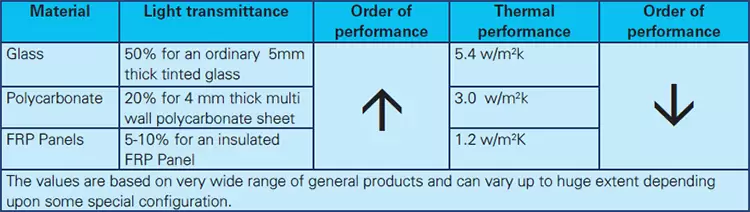
There are two major classifications on selection of skylights, says Abhishek kumar Sinha: one is based on design requirement for daylight within allowable limits of heat gain (through heat conductance and specific heat gain) and other is based on material. At present, the material choices available for skylights are Safety glass, Polycarbonate sheets and FRP (fibre reinforced plastic) Panel. Each of these materials has its own advantages and disadvantages and require specific skills for installation. All materials have different performance characteristics with respect to light transmittance and heat conductance per unit area exposed to external environment. As a thumb rule, with better thermal performance of a skylight material, the light transmittance is reduces.
Selection of Glazing : The term “glazing” has a very wide range of meanings in architectural vocabulary, including transparent, translucent and even opaque material in its range, says Sinha. Low maintenance glass is only a commercial term; there are coatings available commercially which reduces the dust accumulation on glass surface and thus require less maintenance with respect to cleaning of the glass.

The supporting system or assembly design for glazing
The market has a variety of options of glazing materials ranging from plastic to glass, says Akhila. This selection should be done considering the following facts:
- The direct sunlight diffused through the material or transparency
- The amount of light that comes through or visible transmittance
- The amount of radiant heat transmitted through the material measured by solar heat gain coefficient
- The amount of heat from the air that will pass through the material unit measured by the U value of the assembly
The supporting system or assembly design should be done considering factors such as available sizes of glazing material, span, structural strength of assembly, ease of installation, maintenance and pleasing aesthetics.
Based on what we described above, a glazing material with a low Solar Heat Gain Coefficient (SHGC), low U value, high visible transmittance, and appropriate transparency based on location and layout would be ideal for design of a space, observes Akhila. Other factors to consider are strength of the glazing material, maintenance levels, resistance to breaking or cracking, and how the material will age over time, she adds.
In India, a major problem with skylights is the potential greenhouse effect in the space enclosed, rather than heat-loss. Along with orientation of skylight, heavy tinting of glass or polycarbonate glazing also reduces daylight, contradicting the prime objective of having a skylight. During selection of glass or poly-carbonate glazing, it is critical to optimize light vs heat gain characteristics, adds Roy.
Arijit Ghosh too agrees with Roy. According to Ghosh, glazing should be primarily of Low E Glass (low emittance). Any tinge in it would get you a desirable colour of daylight to enter. DGU (Double glazed units) with thermal barrier are a must in extreme hot conditions. Ceramic fritting, staining are other kinds of treatments are also opted for by designers for façade glazing.
Glass installation too should be done skilfully. Thermal stress glass breakage occurs when there is a temperature variance in different parts of the glass, says Akhila. It is most common in large pieces of sealed insulating glass with heavy heat-absorbing or reflective coatings. The outside of the glass heats up more than the inside as the coating converts radiant heat from the sun into sensible heat. The outer glass expands and bends and when held in place in a rigid assembly cracks. As this breakage is not covered by most glass manufacturers’ in warranties, it should be considered in the design stage itself.
Design of skylights and their actual performance must be validated by using computer simulation tools. Computer Simulations must be carried out to analyse and quantify both these aspects for finalization all the design parameters of skylights including their size, location, form and material.
Heat Loss/Gain through Roof & Skylights
The heat loss or heat gain through roof and skylight is an important issue since both together constitute a major portion of building envelope. While, the heat gain or loss is dependent on climatic condition where building is situated, material property is equally important in either condition, points out Architect Abhishek Kumar Sinha.
Heat gain or loss is directly dependent on thermal comfort of inhabitants resulting in more consumption of energy to maintain designed inside conditions. It is a common practice to run a simulation to assess building energy consumption based on selection of material and that provides guidance to arrive at desired empirical values required to choose correct material for skylight and roof.
While in case of roofing material, it is the thermal performance that is a governing factor, in case of skylights, thermal performance, light transmittance and specific heat gain all together become important. The judicious juxtaposition of all these criteria plays a vital role in selection of right skylight material. It is to be noted that heat gain is not only pertinent for skylights but is applicable for overall fenestration of the building.
The heat from the sun is transmitted into a building as radiant heat and the quantum is a function of chemical structure of the glazing material. Various materials react differently to different portions of the sun’s spectrum. Some wavelengths will be reflected, some will be absorbed, and some will be transmitted. If most of the wavelengths in the infrared and ultraviolet portions of the spectrum are also largely transmitted, then the glazing material will allow almost all of the sun’s radiant energy to pass through into the space below.
As far as the thermal properties of a glass or sheet is concerned, the factors governing the same are the U value – the heat loss performance of the skylight assembly & SHGC – Solar Heat Gain Coefficient. These two factors work together. To explain further, SGHC is the heat gain from sun alone. On the other hand U value also includes thermal gain or loss due to the conditions inside including human body temperature, heat generated from HVAC and other services, heat generated from various equipments that are at work inside, etc. So, in summer conditions, a lower SGHC is more important. While in winter, a lower U value is more important with a justification of higher SHGC, says Arijit Ghosh.
Safety & Security
Skylight Safety should be considered for both scenarios i.e., for the people below the skylight and also for the people working on the roof for maintenance or cleaning etc., says Ashish Jain. Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) considers a rooftop skylight to be hole on the roof surface. A skylight that is accidentally stepped on or fallen onto can break and cause a fall from a fatal height. If skylights are in the vicinity of any work area or walking surface, they must be protected with the appropriate screens or guardrails. Hence, selecting a tempered/laminated glass skylight that is covered by a skylight screen (wire mesh) /guardrail at the top can be a good combination to prevent accidents.
According to Rajan Govind, as a basic requirement, glass must comply with “safety glazing” i.e., use laminated safety glass. Furthermore adequate drainage provisions and roof slope should be considered for compliance with maintenance aspects.
The prevalent safety threats to skylight are design loads (static, snow, wind and seismic), fall hazard and fire hazard. Heavier the material, more the hazard. Safety is always of utmost concern and if the installation locations make it prone to hazards, the most secure option is to go for a material which is lighter and has robust framing system, a material that can sustain fire and external loading and does not disintegrate, says Ar. Abhishek Kumar Sinha.
One of the safety issues with skylight is potential accumulation of smoke in case of fire within the premises. It is recommended to have provision of smoke venting (which can also double up for heat venting) either through natural or mechanical means.
Types of Skylights
Any glazed assembly that admits natural light through a roof can be called a skylight. Some manufacturers use the term ‘roof window’ to describe a relatively large skylight placed low enough that you can see out to the landscape. Roof windows are generally big enough to qualify as means of egress in case of a fire, says Ashish Jain.
Skylights are available in a variety of shapes and sizes. They can be flat, domed, fixed, or vented. Fixed skylights cannot be opened, unlike vented skylights, either manually or remotely.
Tubular Daylight Device (TDD) : Tubular Daylight Device capture sunlight using a rooftop dome, then transfer it indoors through a reflective tube that runs from the roof to the ceiling. From there, the light is evenly dispersed into the interior space using a diffuser. These models, and in-tube solarelectric system collects energy to power a Nightlight that automatically comes on after dark.
Tubular daylighting devices are sometimes referred to as “tubular skylights,” “sun pipes” and “light tunnels”. These are high-performance devices that use patented optical technologies to significantly improve the way daylight is harnessed and delivered to interiors. In future, the daylighting would be tapped and channelised to produce high performance interior lighting. This is an innovation which architects are really excited about. We would like to see designers interacting more with the lighting vendors to come up with these.
Difference between Roof Windows & Skylights : Roof windows and skylights both have the function of introducing natural light into the interiors and brighten up the space. Roof Window is a sloped application of a fenestration product that provides for in-reach operation. They are also used for emergency escape and rescue. Though, a translucent panel mounted at higher level on an opaque façade also termed as skylight, the same cannot be said to be a roof window as it is not mounted on roof. They are widely used in areas where it is not possible to introduce light through windows especially in areas like atriums, corridors, attics, store rooms etc. They can be confused with each other; however, the characteristics which distinguish between the roof windows and skylights are the following:
-
-
- Roof Window is an outward opening window in the roof which allows both lighting and ventilation of the interiors. Skylight is a fixed window in the roof and only allows light into the interiors.
- Roof windows are larger than skylights.
- Roof windows allow access to the roof for any kind of maintenance work while skylights are fixed.
- Roof windows give beautiful views of the exteriors specially when used in sloped roof and bring a lot of nature and sky views from the interiors. Skylights do not provide any natural views.
- Roof windows provide direct light while skylights provide diffused light into the interiors. Square or Tubular skylights are used to bring a consistent quality of natural light throughout the interior space.
Enquire Now for UPVC Fixed Windows
-

Roofing Space Frame with Glass
Roofing
Roofing system is a combination of roofing material that forms a skin cladded over framing system intertwined with the structural system of the building. It is an important part of the building envelope that is intended to essentially provide shelter and protection from rain, heat and wind. Depending on the type of building, roof designs vary and so do roofing materials, says Ashish Jain from AEON. Other concepts which govern the selection of roofing system is behaviour of its components against weathering, thermal properties, ratio of span vs weight, cost and construct ability, adds Abhishek Kumar Sinha from Turner construction. Each kind of roofing system requires a framing system to support various loads including dead load of roofing material transferred safely to foundation system.
Selection of Roofing System
Once the design and selection of roofing system is identified as per project requirement, the cost and durability of the material are major consideration for choosing the right roofing material, says Sinha. The roofing system has huge range starting from conventional Flat/low slop RCC slab, Composite deck slab, sloped roofing of steel sheet, sloped roofing of thatched roof, shingle roofing, roofing with terracotta tiles, glass roofs, etc., adds Sinha. A cost benefit analysis based on the anticipated service life of building, is what one should look at to select appropriate material. For example, Aluminium alloy roof sheeting has more life than Galvanised coated steel sheet, but latter is cheaper.

Skylight- Adding daylight to Raipur Airport
Types of Roof Systems :
The span of a roof with or without intermediate columns should be the designer’s and structural engineer’s first governing factor, observes architect Arjit Ghosh. Concepts of roofing are categorized in terms of accessibility – accessible & non accessible. Derivations of many forms of roof come from the second category.
An Accessible Roof is usually flat with insulation and waterproofing. Insulation is done by expanded or preferably extruded polystyrene. The slope for waterproofing is done in PCC (Plain Cement Concrete) and waterproofing should be with membrane preferably. The life of membrane should be seen before selection. However, there are other traditional forms of waterproofing with lesser life.
For Inaccessible Roofs, sloped and curved forms in various geometric forms are available. The structural part is done in either RCC (Reinforced Cement Concrete), metal truss, space frames or wooden truss. Sheeting materials are shingles, metals like aluminium or PPGI (Pre-Painted Galvanised Iron). Installation of these are vendor specific after the structural component is in place, points out Arjit Ghosh. In addition, there are materials like clay tiles which are smaller in size, shingles made of tar, metal sheets, stone slates etc, which can also be used for roofing.
Enquire Now for Door Frame & Profiles
Corrugated metal and cement sheets in long lengths are mostly used for industrial structures, points out Manish Banker. Then there are unconventional materials like thatch and bamboo. Flat roofs are normally covered with china mosaic made of broken glazed tiles which are vastly used for their waterproofing and heat insulating characteristics. Also we have Tensile Structures where we can attain some extremely dynamic forms like saddle shape or hyperbolic or paraboloid ones that is double curves. The materials are fabricpolyester or fiberglass with coatings. It has the quality of allowing some amount of light to pass through and can be installed with ease using light weight structural systems, observes Banker.
For small span roof structure where dead load is not a governing factor, concrete slab over RCC framed structure is most prevalent choice. A composite deck slab (RCC slab resting on Steel deck as permanent form work) is also another option for fast track projects. Concrete is a naturally well insulated material but sandwich roof slabs have an improved U value and they improve the thermal performance of the building.
For large span roofs, the most prevalent roofing system is sloped metal roofing system, where metal roofing sheets are laid over secondary framing material on the primary structure (trusses or portal beams) of the building. In such systems, choosing right materials is very critical since metal roofs, unlike RCC, are not forgiving systems and require specialized skills and labour. The choice of material for metal roof is primarily limited to galvanized/galv. alum. steel, aluminium alloy and zinc (Very recent).
Metal roof
Metal roof build-up consists of several layers of different materials placed together to achieve specific performances and functional requirements. Hence the designers should have good understanding of all these materials and performances, notes Rajan Govind of BES Consultants. Installation of roof requires specialist skills such that the completed roofs lasts much longer without major maintenance. All these materials offer better corrosion resistance with increase in cost of basic material and coating system.

Tensile Structures can attain some extremely dynamic forms like saddle shape or hyperbolic or paraboloid ones that is double curves
An important selection criteria in the metal roofing system is, explains Sinha, the kind of insulation, the system offers pre-insulated panels as well as on-site insulation where single span roof sheets are required. The roofing assembly consists of sandwich layers of top sheet, insulation (for thermal and acoustic insulation), and vapour barrier and bottom sheet. The geometry of crest and trough for both sheets are also dependent on various factors like annual rain fall data, snow load, slope of roof and the span of purlins. The use of galvalume sheeting without insulation could make spaces very uncomfortable and double skin sheeting with use rock wool insulation is recommended. An alternative to this option is insulated PUF panels which are readily available in the market, advises Akila Anantharamn.
There are new age technologies of rolled metal sheets which can take any shape and are available in many sizes for covering roofs used over buildings having large footprints like airports, stadiums and railway stations.

Cool Roof Solutions
Another important factor to consider in the selection of roofing material is its thermal performance. The U value of a material measures this and determines comfort, ambient temperature and air conditioning load within the space, says Akhila Anantharaman of Geodesic. The key factor to consider in the supporting structure for the roofing is the span and usage of the building. Large column free spans are a requirement in many projects and the most economical solution for such cases is space frame structures. These structures are much more efficient in comparison to conventional framed buildings.
To conclude, roofing materials should be chosen such that they perform efficiently on following aspects:
- Water tightness
- Air tightness
- Low heat ingress
- Low Surface temperature
- Low maintenance
- High strength
Trends in Roofing
Latest trends in roofing include developing solutions that can achieve a balance between human comfort, energy efficiency and energy generation, comments Jain. Roof, being the topmost surface, receives maximum solar radiation that leads to higher heat loads and space cooling requirements on top floor of the building, which means higher energy consumption and lower human comfort. Additionally, in today’s world of limited site areas, roofs have become more than a shelter and are used for landscaping, recreational activities and even renewable energy generation while allowing lesser heat dissipation to the floor below. Some fast growing concepts of roofing include Insulated roof, Cool Roof, Green Roof and Solar Roofs, adds Jain. Insulated and cool roof solutions have been developed to a reasonable level. However, Green Roof technologies that are low cost and need low maintenance will be a great advancement in today’s age where roof spaces have become more valuable and habitable.
According to Ar. Sinha, the prevalent material for roofing is standing seam metal roofing (SSMR), where a single length metal sheet covers the entire length offering a seamless puncture less roofing sheet. The length of sheet can go up to 200 meters. Adjoining panels are seamed together using a male-female configuration, allowing a puncture less joint, negating the chance of leakage unless a situation arises which is taken care by virtue of roof’s high slope. Further, the sandwich configuration allows addition of more layers between top and bottom sheets, and thus can be customized as per requirements for thermal insulation and acoustics.
Certain roofing materials are yet to achieve commercial success. These materials do not require a secondary support system since the material itself has innate capability to withstand the required span and loads. Inbuilt solar panels, vegetative roofs, reflective colours to reduce heat gain are another innovations.
For Ashish Jain, the favourite roofing materials are – Insulated roof tiles for non-habitable roofs and blend of vegetated and light coloured surface materials for habitable roofs. Insulations and cool roof solutions have been developed to a reasonable level. However, Green Roof technologies that are low cost and need low maintenance will be a great advancement to watch for, he adds.
Enquire Now for Solar Panels
In the modern day context, complex geometric forms are what designers are experimenting with. 3D design softwares have opened up a whole new world for the designers to detail their designs much faster and easily than ever before, observes Arjit Ghosh. As such, space frames with sheets – glass and polycarbonate, and tensile roofs with fabrics are trending today. His personal favourite for roofing is glass on trusses / space frames.
Rajan Govind also agrees that complex shapes and interesting architectural forms and geometry in roofing are the latest trends. New generation design requires roofing design to be integrated well with building geometry.
Most Common Problem Spots in Roofing & SkyLights
Abuse of material is biggest problem area in roofing and skylights, says Abhishek Kumar Sinha. Overuse and unjustified selection of materials to a particular context possess huge threats. It also maligns the image of such system and causes prejudice to the public in general.

Green Roof
Manish Banker points out that waterproofing and the need for water proof/weatherproof joinery is also a key issue. Further, installation with incorrect material /incorrect method also causes major problems. Poor maintenance, primarily attributed to lack of access path for maintenance, becomes problematic. Ashish Jain suggests that integrated contracts of complete installation and maintenance of roof systems can be a solution to overcome these challenges.
Malfunctioning of roofing and skylights are generally found to have source in workmanship and design rather than failure of material to a greater extent, adds Sinha. Ashish Jain and Rajan Govind too agree that poor workmanship in the installation of insulation/cool roof, especially with waterproofing as the key challenge. Arijit Ghosh too points that lack of knowledge on the part of the designers in terms of choosing material with optimal specifications and bad detailing on part of the execution team & the vendors as key problems. This shall be addressed with enhanced and well trained roofing implementation agencies and uses appropriate techniques at the building site, opines Govind.

Glass Dome for temple at Kudal, Maharashtra
Conclusion
Energy efficiency, water tightness, sound reduction and other factors such as load and wind resistance are important considerations while choosing design and materials for skylights and roofing. Explore additional options such as shading, UV coatings and ventilation Modern roofing and skylight could become the future of smart homes by improving indoor climate through technology. Studies reveal that 90 per cent of our time is spent indoors and poor indoor air quality and lighting could affect productivity drastically. Hence it is essential to educate oneself with above mentioned helpful tips before selecting the design and installing skylights and roofing.

Skylight and Roof at Vadodara Airport























Post A Comment