
Curtain Wall Systems
With urbanization inclined perpetually towards fostering construction of multi-storeyed buildings in metropolitan and developing cities, façade selection emerges as a critical component. Modern façades have to incorporate functionality, durability, aesthetics and energy conservation. Building envelopes, including curtain wall systems, ventilated façade systems and sun shading systems, are all combined structurally in order to manage durability, lasting functionality, light dissemination, water, air and sound insulation, thus preserving energy efficiency of the structure.
Post your Requirement
Enquire Now for Cladding & Facades
Curtain wall systems, non-structural cladding systems for external walls, are closely associated with the modernist movement in international style. In this story, we present approach to design curtain wall systems, key factors to be considered during design, cladding elements,issues affecting performance, optimisation, latest technology in the field and on intelligent glazing systems for curtain walls.
Design of façades depends on multiple factors. Apart from budget and overall aesthetics, design feasibility and contextual factors such as surrounding buildings, climate, end-users comfortability, interior atmospheric quality, thermal equilibrium etc. play a crucial role. The building must positively respond to all these dynamic factors.
Deciding On the Type of Façade
Façades are not just the building‘s skin, they are its face as well. Beyond functional aspects, aesthetic considerations also play an important role and, sometimes, an ambitious client’s aggressive demands lead to extreme designs. Selecting optimal materials opens space for creative design without compromising on engineering needs in the process.

Ar. Khozema Chitalwala,
Principal Architect of
Designers Group
Before delving into the extremes of design intervention on the façade, it is vital to know the matter of availability of material and manufacturing technology for such design. The type of façade depends on the building type and contextual climate, says Ar. Khozema Chitalwala, Principal Architect of Designers Group.

Mathieu Meur, Managing Dire-
ctor, Meinhardt Façade Techn-
ology (S) Pte Ltd
Façade consultant Mathieu Meur (Managing Director, Meinhardt Façade Technology (S) Pte Ltd) observes that deciding on the type of façade to adopt the best design and materials requires close collaboration between the architect, developer and façade consultant. While the architect sets the aesthetic direction, the developer provides the brief and budget and the façade consultant puts it all together by providing technical advice on the various options that can be considered.

Uttaran B Ray, Founder & Man-
aging Director, Studio Form
Techniques Pvt. Ltd.
Uttaran B Ray (Founder & Managing Director, Studio Form Techniques Pvt. Ltd.), who is into boutique façade design, engineering consultancy & turnkey contracting, also points out that architect provides detailed design intent. Consultants develop upon it further to make it practical and feasible. “We derive the type of façade through a design dialogue between the architects and us. Façade consultant’s role is to approve or comment upon the interface details and structural calculations that we submit. The role is limited to performance and not really the look and feel of the envelope”, adds Ray.
Thus, we understand that architect has the upper hand in designing and consultants work on it to make it practical and viable. Façade fabricators are obliged to go by the tender drawings/specifications and the room to influence type of façade is minimal.
The Key Parameters

Akshat Bhatt, Principal Archi-
tect, Architecture Discipline
The building elevation is the first level of dialogue with a user, says Akshat Bhatt, Principal Architect, Architecture Discipline, a New Delhi based firm. It is important to understand that the elevation has to express concerns of the development and the program. He emphasizes on the importance of engaging in bespoke engineering and refined detailing in order to ensure an expressive elevation as opposed to a generic component.
The façade of a building is the essence of what the building stands for and selection of façade design is an experiential process, says Bhatt. “We need to contemplate on the views of people as they see the building, analyse speed of cars passing by, climatological parameters etc. After considering all such parameters, we develop a building skin that has a strong architectural expression and meets the technical performance criteria”, adds Bhatt.

Gaurav Gajjar, Design Team
Leader, Alfanar Aluminium,
Riyadh, Saudi Arabia
According to Gaurav Gajjar, Design Team Leader, Alfanar Aluminium, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia, façade type selection is centrally driven on the basis of project peculiarities such as architectural concept, geographical location of the project, environmental factors prevalent at site and the end user. The system type and design is dependent upon these factors and not a single aspect could be missed or taken for granted if the project is to succeed holistically.

Nicholas Goldsmith FAIA LEED
AP, Senior Principal, FTL
Design Engineering Studio
Nicholas Goldsmith FAIA LEED AP, Senior Principal, FTL Design Engineering Studio, says that while developing a façade, the architects would look at the building physics, orientation of the site and proposed buildings, climate zone and environmental challenges. They would provide us a sense of building mass, openness and desired transparencies.

Hans Brouwer, Principal Archi-
tect, HB Design Pte Ltd
Hans Brouwer (Principal Architect, HB Design Pte Ltd) points out that the design of any façade system should be determined based on a rigorous investigation into the key performance criteria and the most appropriate ways of achieving these. It is never the result of purely aesthetic concerns.“In addition to the environmental performance of a façade system, we also need to take into account capital investment costs as well as downstream operational costs. All 3 elements need to be looked at holistically to determine the best solution for each project,” he adds.

Santanu Duttagupta, Project
Manager, Design2Occupancy
Services LLP
Santanu Duttagupta (GRIHA Trainer & Evaluator, IGBC AP), Project Manager, Design2Occupancy Services LLP, is certain that durability or life expectancy is the key factor while designing a façade system to resist environmental loads. But selection and design of the façade system depends on the building type, size, usage, ownership and management team. But from the sustainability point of view, optimization of daylight and reduction of heat ingress are most important influencing factors.
Khozema Chitalwala too agrees that the type of façade should be simultaneous with the building system profile. Although desired as something specific, the façade still depends on other intrinsic factors that include building type, easy maintenance, design style followed, thermal conductivity, availability of material in the market, operative performance, acoustics and above all assurance of safety and shelter.
Design factors must fundamentally focus on having a healthy interface between the external & internal environments, meeting the desired aesthetic intent, being simple to install/repair/maintain, adequate design strength to bear the wind loads/ live loads/seismic loads/snow loads/thermal loads, says Gajjar. The objectives for a healthy interface relation between external & internal environment are controlled by effective water proofing, thermal efficiency, air tightness, condensation proof, acoustical insulation, maximizing natural light intake, he adds.

Pride World City Sales Offi ce at Charoli – Designers Group

Discovery Centre, Bengaluru – Architecture Discipline
According to Santanu Duttagupta, Wind loading depends on the complexity of the building design. A wind tunnel study is important to understand the wind pressure. A full scale laboratory test can be done to check Seismic loading. Thermal performance and moisture condensation resistance capacity have to be verified to analyses thermal loading. Visual light transmittance is one of the most important factor for occupant comfort and indoor environment quality. Optimization of daylight and direct indoor outdoor visual connect are important factors as far as sustainability and green buildings are concerned. Routine maintenance is necessary to make sure the performance of the curtain wall system. Durability is measured by various structural checks (in line with above mentioned load factors) which are done prior to design finalization.
Curtain wall designers also need to be aware of practical aspects of curtain wall fabrication and installation (e.g. maximum die size available, glass stock sheet sizes, metal panel sizes, etc.), opines Mathieu Meur. In addition, there are various regulatory requirements that apply to curtain walls, and these vary from country to country. For instance, some locations limit external reflectivity of glass, or set a maximum U-value and g-value that can be used. In other cases, certain materials are prohibited. All in all, curtain wall designers need to be highly versatile and experienced in order to achieve a successful outcome.
Durability and Sustainability
Durability and sustainability is measured by quality of systems and materials which are recommended. We generally take into account various material interfaces and long term performance. Information from manufacturers is critical in the recommendation of systems.
Durability and sustainability factors are researched upon at the design bid stage, which may go through many iterations to achieve the overall design intent, opines Uttaran B Ray. Available experimental data is trusted to estimate reliability of finishes, corrosion resistance, material integrity/ compatibility, sealant degradation etc., says Gajjar.
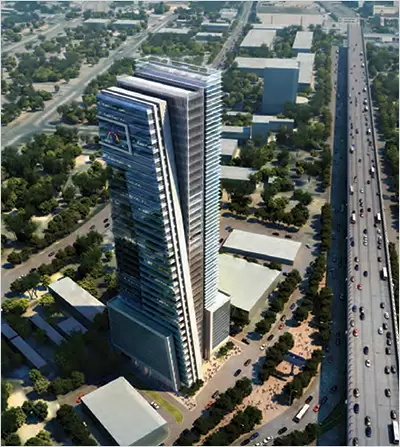

AKH Tower, Dammam, Riyadh
Curtain walls are built to last longer, but are liable to have life expectancy issues if not maintained properly. Glazing, being braced on aluminium frames (malleable hence design friendly), is to be given a specific fluoro polymer coating or else would environmentally degrade. Sealant corners are prone to abrasion on prolonged exposure to moisture or heat. Along with good design principles, it becomes important for the walls to have high resistance and low emissivity values for prolonging service life.
It is observed that bad workmanship and bad design are two main causes affecting durability of curtain wall systems, explains Dutta gupta.
Steps to prevent bad workmanship:
- Certified and experience installers must be engaged
- Regular on-site inspection required
- Check installation sealants, fixings, gaskets, etc.
- Review of storage and handling of the pre-cast units
Steps to avoid bad design:
- Design life consideration
- Understanding of building physics
- Adequate movement of the joints
- Environmental considerations – mock ups and inspections
- Research the product materials.
- Design façade in harmony with the structure.
Good design specs and planned maintenance are the other factors to ensure façade durability.
Sustainability for any given project could be best achieved by fine-tuning the material selection/ sourcing for façades. Materials which are produced locally (ideally within a circular periphery of 50 km) and which are easy to decompose within a time frame threshold to the building design life period becomes the ideal choice. This way the sustainable buildings will not generate a residual balance to the environment upon demolition.
Selecting Between Stick and Unitized Systems
To better evaluate selection criteria, let us first understand the basic difference between Stick and Unitized Systems. In Stick systems, the individual mullion and transoms are machined in factory and the assembly with glass, pressure plate, accessories and cover cap takes place at site. The mullion-transom installation over the brackets, anchored to slab, takes place resulting in a structural grid work. This makes the system performance quite dependent upon the installation workmanship at site and necessitates the requirement of a dedicated scaffolding arrangement for installation.

AL Sebei Hotel (Train is the design theme)
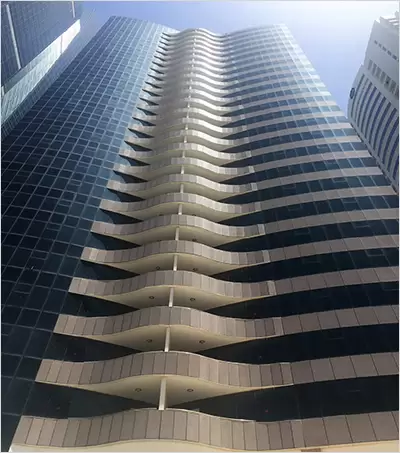

Noor Tower, Qatar, Doha (SMARTIA M50 from ALUMIL): Structural stick type curtain wall system, outstanding design and high energy effi ciency
Unitized curtain systems can have multiple infills (ex. operable vent). They normally work best when the façade design involves a high degree of repetition. On the other hand, for low-rise constructions with limited repetition or a small number of panels, stick systems make better sense.
Cladding Materials for Curtain Walls For curtain walls, any material from plastic to fabric to stone could be used for cladding. Selection of material depends on requirement of expression and performance.“We have started using new age composite materials and carbon fibre in recent projects”, says Ar. Bhatt. Glass is the most widely used infill material due to excellent light transmittance characteristics. Use of glass reduces internal passive lighting requirements, observes Gajjar. Glass is durable and comes with wide ranges of colour and thermal properties.Desired aesthetics is the primary criterion for selecting infill material. Once required aesthetics has been established, several possible options are reviewed in the light of the other criteria including structural adequacy, durability, availability, cost, thermal performance, etc. Infill materials could be fabric veneer, stone veneer, panels, louvers etc.,
says Dattagupta. Accordingly, infill materials could have matt, satin or glossy texture.
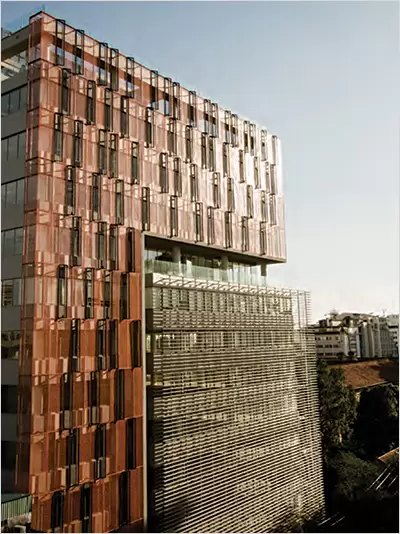

President Place, Ho Chi Minh, Vietnam
We distinguish between “vision panels” and “nonvision panels”, says Ar. Hans Brouwer. Where transparency (views out) and light transmission (natural lighting in) are required, vision panels are specified. In other conditions, the options for cladding material can be wide ranging from stone, to laminates to metal screens.
Enquire Now for Laminate Sheets
For cases where the solar light is not desired, there are wide range of choices available like ACP (Aluminium Composite Panels), Solid metal cladding like Aluminium wall cladding, Stainless Steel, Copper, Zinc, Titanium and Br, ceramic/porcelain/ clay, high pressure laminates, tensile fabric, GRC(glass reinforced concrete), ETFE, corten, etc. Here,
selection criteria depends upon the architect’s intent and the theme being iconized for the project. For glass selection it is good to have low solar factor & U Value and high light transmittance.

An integrated glass and membrane curtain wall for the Central Library in Phoenix AZ, USA, by FTL Design Engineering Studio
Materials can be combined to give a special look to the façade. Besides conventional glass with infills being combined with brick and concrete to create innovative building envelopes, other cladding fills like terracotta, thin stone, HPL (High pressure laminate), WPC (Wood plastic Composite), GRFC (glass fiber re-in forced concrete), etc. are selected to produce experimental skins on the building, notes Chitalwala. Meur considers GRC, GRP, solid surfaces, phenolic panels and other exotic materials for curtain walls other than stone and ACP. Nicholas Goldsmith says that their specialty is working with ETFE (Ethylene tetrafluoroethylene) foil cushion systems and fabric shading which can be used in conjunction with glazing systems.
Enquire Now for High Pressure Laminates (HPL)
According to Ray, Corten steel screens have large demand. Though there is an issue of staining due to a water run-off, it requires almost no maintenance while seasonally changing various tones of oxidation (rust!) Un-sealed copper is another such favourite with similar properties. Other existing processed materials include complex geometry formed acrylics and solid surfaces which are UV rated. Another trend that we notice is the requirement for energy related performance skins.
Prior deciding the cladding material to be used, one must also consider how the visionary access (opaque, translucent, transparent) goes in tandem with other instances such as reflectiveness, choosing the type of glass (triple glazed/double layered), its thermal conductivity, exchange of light, heat and air, responsive outcome of an altering climate (day and night), the need for a sustainable integrated façade, etc. The market availability and constraint on manufacturing could collide with the planning and completion time as well. However, since each material exhibits different properties based on the above list, it is essential that the whole vertical curtain performs as an entwined system.
Safety is also important selection criteria. For the balustrade, skylight or children play area applications, laminated glass is an ideal choice. Post breakage, laminated glass has the ability to hold the broken glass pieces in place thereby minimizing direct injury risk, says Gajjar.
Key Factors Escalating the Performance of Façades
According to Dattagupta, design is the most important stage to optimize the performance of a curtain wall. We need to study the building’s profile and orientation. Shadow analysis and sun path analysis are important. One needs to consider heating cooling load and daylight too before the selection of best façade material/combination. Façade maintenance aspects are also crucial. Ar. Chitalwala too agrees to this. In addition, one need to consider energy exchange loads, glazing ratios, periodic changes of shading according to overhangs, etc. These aspects, well in accordance with the building’s profile, need to be clubbed with the occupant’s productivity and well-being.
It is important to understand both the inside and the outside of a building’s façade to evaluate it correctly. Some of the essentials for performance evaluation are: daylight ingress, night time expression, heat bridges and dew points. The architect’s skill really lies in being able to translate building physics parameters into an expressive construct, says Ar. Bhatt.
Gajjar points out that the most critical factor improving performance of a façade is its ability to provide efficient weather proofing,to enhance the solar performance the façade, the material must have a higher resistance to the heat flow i.e. lower U value and a lower solar factor applicable for glasses. Pressure equalized rain screen principles play a vital role in enhancing the weatherproofing and thermal performance of façades. Another crucial aspect to consider at design stage is accessibility for maintenance.
Thermal Performance of Curtain Wall Systems
Thermal performance of curtain walls play an important role in resisting the inflow or outflow of heat energy. For the projects in hot regions, the objective is to reduce the solar heat influx to reduce the cooling load. Whereas in cold regions, it is imperative to retain the internal heat to reduce load on heating systems. According to Meur, in a high-rise air-conditioned building, the façade can contribute in the range of 30 per cent of the total heat load on that building, with the rest coming from internal equipment, human occupants, etc. If the building envelope is made 30 per cent more efficient, then this could represent a reduction in the total heat load on a building of about 10 per cent, which is substantial.
According to Gajjar and Dattagupta, thermal performance of façade systems could be improved by incorporating a non-metallic, low conductivity infill material to create an insulating effect. Common insulation infill materials used are polyamide (PA) and polythermide (PT).
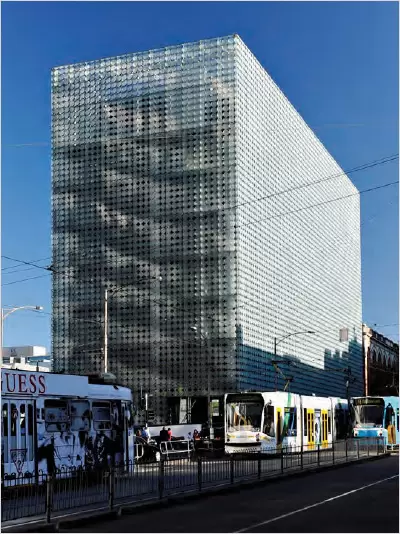

RMIT Design Hub, Melbourne by Meinhardt – The glass shading disks are individually controlled via a computer so as to optimise daylight harvesting and minimise heat gain
PA has better thermal performance and rigidity then PT; however, it is twice as expensive as PT. Another way to enhance the thermal performance of system is by increasing the number of gasket and its contact with the AL section or by having more air pockets. Use of soft coat, low E coatings have a major impact on solar passive heat gain.
Thermal conductivity of the curtain wall is important as the heat loss/heat gain directly affect the heating/cooling cost of buildings. To improve performance, thermal breaks of are incorporated. Pressure bars are also used in some of the systems. Maintaining the continuity of the air barriers at the perimeter reduces airflow around the curtain walls. Aluminium is normally used for curtain wall framing due to its light weight. However, heat transfer coefficient of Al is high and therefore there is a tendency of heat loss/heat conduction through Al curtain wall mullions.

Pride World City Sales Office, Charoli, Pune – Designers Group
Reducing Construction Cost
Repetition of details and modules brings down the cost of façades, says Meur. Unusual modulations, particularly very large or non-rectangular panels, contribute to additional costs due to excessive wastage and higher shipping charges. The unit rate for granite from Brazil or a travertine from Italy is higher than that of a composite aluminium panel, for instance. Interestingly, some developers want to explore adopting window walls (floor-toceiling glazing) as a cheaper alternative to curtain walls. This may not necessarily be effective, as window walls require more brackets, anchors and sealant, scaffolding for external access, and more importantly, they reduce the NLA (net leasable area) substantially. The same applies to increasing spandrel areas to save on supposedly more expensive vision glass.
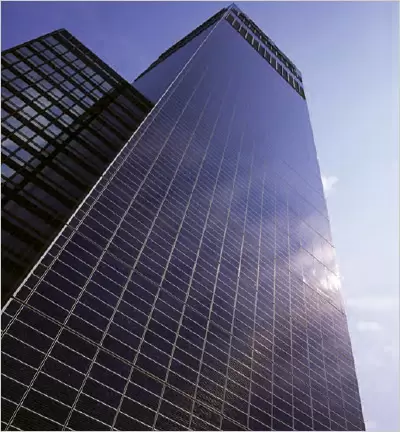

CIS Tower, Manchester: BIPV (building integrated photovoltaics) on façade
While it is true that monolithic or laminated spandrel glass is cheaper than a double-glazed vision area with coating, the unit rate for spandrels is often higher than that of vision areas when you factor the additional powder coated back-pan and foil-backed insulation.
Latest Technologies and Trends in Curtain Wall Systems
Development of more “intelligent” glazing systems have radically altered the energy balance of traditional curtain wall systems. Double-glazing has improved insulation values significantly and intelligent coatings, such as low-e, have reduced the impact of direct insolation (sunlight coming into the building) and the resultant heat loading on the interiors.
The nascent trend of façade integration that includes amalgamating various power influx techniques providing energy-efficient buildings, are gradually taking lead. In response to keeping the interior air quality comfortable, these active façades tend to perform strategic mechanisms that control solar heat gain/glare infiltration, effectual ventilation, harvesting daylight, thereby reducing the building’s gross energy consumption. Some examples include rain-screen façades, BIPV (building integrated photovoltaics) (CIS Tower, Manchester), automated shading and transparency controls (Eskenazi Hospital, Indianapolis), effective day lighting, multiple infill unitized systems, Nano coated ACP (in gulf countries), etc.

Antony John, Engineering
Director, Schueco India
According to Antony John, Engineering Director, Schueco India, following are the latest technology in curtain wall systems:
- Slim façades with less than 50mm face width
- Concealed slim width to tall open able
- 60mm face width unitized façades
- Parametric façades where the Architect’s vision for truly 3D façades can be fulfilled.
- Modular façades: Easy up gradation from basic to very high end thermal and acoustic requirements within the same façade. Mix and match of façade face width to suit architect’s need for emphasis and iconic designs.
- Façades designed with advanced software: Integration of design, shop floor and site installation using advanced software’s. Next generation post BIM.
- Smart Façades: Holistic integration into the building maintenance system of internal and external shading devices, control of solar heat gain coefficient through glass such as sage glass, ventilators and exit devices.
Factors Responsible for the Failure of Curtain Wall Systems

Eskenazi Hospital, Indianapolis – Dynamic façade
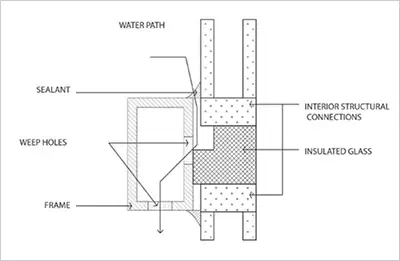
Proper waterproofing techniques for curtain walls
Another source of failure is the design of the curtain wall itself, says Meur. This is more critical, as any mistake in the design of a panel gets repeated throughout the façade, resulting in the system failure. Other main factors of façade failures are wrong or no structural analysis, interface details which are not practical and achievable.
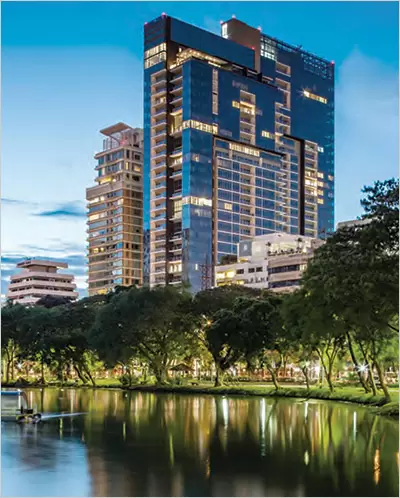

185 Rajadamri, Bangkok – HB Design Pte Ltd
Conclusion
The selection criteria for the type of curtain wall system is dependent upon the manufacturing, installation & performance aspects of the respective system versus demands of project. Factors ranging from simple glare discomfort to a major structural collapse define the quality in curtain wall systems. There is a significant shortage of skilled technicians to carry out appropriate installation and proper quality control. Poor performance of curtain wall is often due to misunderstanding of fundamental principles of façade design and structural concept of curtain walls by construction parties, and gaps of oversight and coordination in the established project delivery routines.
Curtain Walls Should Meet all the Performance Specifications

Hemjith A Vengateri, Managing
Director,ALUMIL Systems
India Pvt. Ltd.
WFM: Please brief on the factors to consider while designing curtain wall system for a building? How do you ensure the durability and sustainability of curtain walls?
Hemjith A Vengateri (HV): First of all, an elementary study is done to decide on “grid façade” and during this study, the type of the curtain wall – stick, structural glazed or unitized – is decided. Other factors taken into consideration are architectural trends, budget, and completion time. All the performance specifications for water tightness, wind load resistance, thermal insulation, as well as other specifications such as sound reduction, fire safety, anti-vandal & bullet proofing, etc. are to be met.
The following aspects should be taken into account while selecting a curtain wall type:
- The architectural intention -purpose
- Need of highly glazed façades
- Narrow frames
- Horizontal or vertical framing emphasis
- Geometry complexity
- Quality level
- Erection area
- Erection time
- Cost factors
- Choice between Stick type and Unitised curtain wall systems.
ALUMIL has a notably wide range of products such as SMARTIA M5, SMARTIA M6, SMARTIA M65, SMARTIA M50 and SMARTIA M7 which offer great performances and value-for-money solutions.
WFM: How can you use Aluminium as an efficient curtain wall material?
Hemjith A Vengateri (HV): Aluminium is a great modern construction material, with multiple advantages making it clearly the best choice for effective curtain wall systems. It is a light yet strong material, which is crucial for a safe construction of highrise buildings. It is also 100 per cent recyclable and thus enables LEED certifications, contributing significantly to the protection of the environment. Moreover, it is a flexible material which leads to faster and easier construction procedures, minimizing overall construction time. In addition, although aluminium systems are characterized by their thinness, through special embedded polyamide profiles and other materials, they provide impressive thermal break performances offering high thermal insulation. Lastly aluminium provides infinite design and surface treatment options, giving to architects a wide spectrum of aesthetic possibilities and expressions.
WFM: What is the criteria for selection of cladding material including glass and aluminium?
Hemjith A Vengateri (HV): As you may realize, there are many criteria for selecting aluminium cladding & glass cladding as materials. Some of the most important criteria are:
- Unlimited manufacturing options in any shape and size in terms of width & height (for small or large spans).
- Vast possibilities of surface treatment as for example powder-coating (all RAL Durable & Ultra Durable colours), anodizing (with special effects such as satin, gloss, mat & various combinations), or wood imitation painting),
- High durability with minimum maintenance requirements.
- Environmentally friendly – 100 percent recyclable materials
- Robust and rigid frames without the need for additional steel reinforcement.
- Design freedom with infinite creative combinations of aluminium and glass.
WFM: Please brief on the key factors escalating the performance of façades?
Hemjith A Vengateri (HV): The most crucial performances for façades are the following: air permeability, water tightness, wind load resistance, thermal performance (Uf), sound reduction level, fire safety, anti-vandal, & bullet proofing.
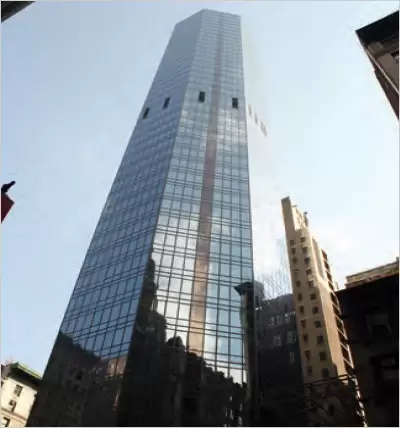

A building on Madison Avenue, New York: Special customized unitized curtain walls system

Poland, Lodz – Philharmonic Hall – SMARTIA M50: Structural glazed façade, excellent thermal insulation & high water tightness
Hemjith A Vengateri (HV): Curtain wall systems can nowadays have “smart” functions, especially thanks to IoT (Internet of Things) technologies. Through advanced electronic systems, special sensors can be built into the curtain wall system, giving the ability to the curtain wall system to “feel” what is happening at the external or internal environment of the building and react to it. Automated actions can adjust ventilation, detect smoke presence and block it, regulate light transmittance or shading. All of these actions can be controlled effectively by special integrated building management systems (IBMS). BIPVs (Building-Integrated Photovoltaics)on façades can be used to generate notable amounts of electrical power, giving to the building a considerable energy autonomy. Generally, smart and environmentally friendly technologies which contribute to building energy efficiency will be definitely the future of curtain wall systems.
WFM: Please brief on thermal performance of curtain wall systems?
Hemjith A Vengateri (HV): One of the most important technical characteristics of curtain wall systems is the thermal insulation performance, following the trend of the lowest possible Uf value. It is very important when designing a curtain wall system to achieve high energy efficiency, without compromising on other performance characteristics. Moreover, through special software that calculates U-values and simulates façades and glazing (e.g. surface size, radiation), it is possible to create curtain wall systems that fully comply with the European and other international norms, by predicting accurately temperature, moisture and condensation levels. Also, new hi-tech materials like aerogels, can be used as infills for high thermal insulation and fire resistance.
Technology has Enabled Easier Analysis of Façade Performance

Nitin Bhatia, CMD & Principal
Consultant, FACET Façade
Consultancy
WFM: How do you decide upon the “type of façade system” for your project?
Nitin Bhatia (NB): A façade is the principal front of a building visible to the outsider. It is a set of things that come together and form the “whole front / elevation” of a building. It is the coming together of profiles, infill panel, accessories, the method by which they are combined or joined, fabrication to facilitate implementation of façade design principles such as rain screen, pressure equalisation, drainage, and system ventilation etc.
In order to decide the type of façade system that should be used on a project, one would need to determine the functionality; to keep weather out or noise out? Or to be a safety barrier? Should it allow view from out to in or vice-versa? Should it be a fire barrier? The answer could be all or a combination thereof.
WFM: Please brief on the key factors considered to enhance performance of façades?
Nitin Bhatia (NB): Design is perhaps the most important factor that determines how a façade system performs. Unlike popular belief, design is not just structural adequacy of various members, but includes joinery, incorporation of design principles such as pressure equalisation, rain screen, glazing cavity drainage, ventilation, etc.Other than design, key criteria that enhance performance are materials and a stringent QA / QC protocol.

Worldmark, Gurgaon
WFM: According to you, what is the latest technology in curtain wall systems?
Nitin Bhatia (NB): The evolution of computational technology has had an enormous influence in evolution of façade technologies. Adaptation of complex and organic geometry as a result is a lot easier today than it was in the yesteryears simply because of the ease of drawing and analysing what you want to achieve. This technology has also enabled easier analysis of performance of systems and therefore optimisation of form and material, and reduced reliance on development of life size samples and mock ups. Other technologies that are evolving are BIPV (building integrated photo-voltaic), interactive media screens having glass infills, etc.
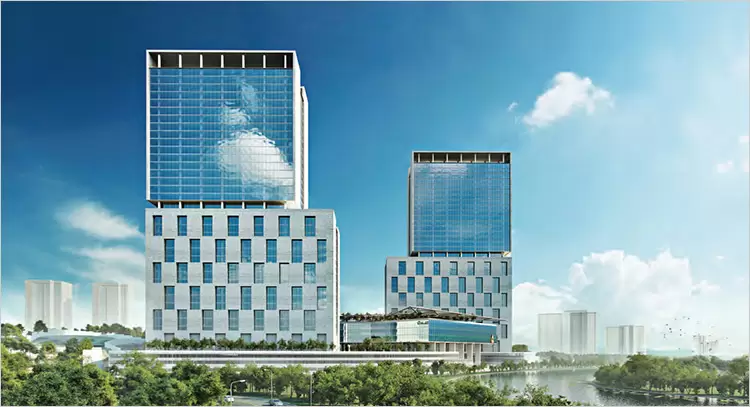

Day & Night view of the Smart city Project at Kochi by FACET Façade Consultancy
WFM: Which is better – installation from the Interior or exterior?
Nitin Bhatia (NB): We firmly believe that the easier it is to do things, the better they get done. Therefore, whatever can be installed from the inside of a building will be a lot easier and better done than installation from a scaffold or cradle.
WFM: What are the most common factors responsible for the failure of curtain wall systems?

Nitin Bhatia (NB): Failure is perspective.Conventionally, only structural failure is referred to as failure of the curtain wall. However, failure is wider than what is conventionally believed. Any factor that affects human comfort adversely should be referred to as a failure. A very common example of design failure is vibration / shaking of large shop front glass panels when pressed, at most retail spaces. Another one is allowance of excessive light through glass that causes glare resulting in squinting.
Climate Responsive Design is the Key

Ar Sandeep Shikre, SSA
Architects, Mumbai
WFM: How do you decide upon the type of façade for your project?
Ar Sandeep Shikre (SS): The decision on the design of the façade depends on the size of the building, complexity of the project and also on type and functionality of the project. Another important aspect is the micro climate response. Façade is to provide a shelter for all the built forms for a habitable use. So the location of the project has a great influence. The climatic condition of the location and lux level also have influence on the design of the façade.
To summaries, the factors which normally influence the decision of the type of façade are use of the building, shape and form of the building, and micro climatic response.
The look and feel of façade -aesthetics – has a very important role to pay. Visual identity of the structure is decided by the façade. Façade is the face of a building. So the decision on façade is a collative, collaborative integrated decision.
WFM: What are the factors which you consider while designing curtain wall system for a building?
Ar Sandeep Shikre (SS): One needs to be very careful while designing the curtain wall with respect to the direction of sun. Hence we can conclude that, the microclimate response, orientation of the building, size, shape and height of the building, and most importantly, the use of the building influence the design of curtain wall system.
WFM: How to decide on single curtain wall and double skin curtain wall?

Institute of Management studies, Mumbai
Ar Sandeep Shikre (SS): Double skin curtain walls are very expensive. They are recommended for complex buildings or high intense buildings. It is like the cavity walls in olden times, seen in Taj Mahal and Hawa Mahal. The same philosophy is applied in modern construction where you have two schemes of glass. The external layer of glass reduces heat penetration. Cavity between two layers of glass acts as insulation.Heat trapped between the two layers is evacuated through mechanical means.
Sometimes, motorised panels are installed between the layers so that they move according to the sun path, which will ensure that no unwanted heat is precipitated inside the building. This system is more suitable for tall buildings. As you go higher, the lux level increases and there should be better strategies to insulate the building. Otherwise, for a low-rise building, single skin curtain wall with DGU panels are good enough. The DGU panel has two glasses with a cavity. Generally, the glasses used are high performance glasses with low-e coating or a double/triple silver coating. This coating allows the glass to enhance its shading coefficient, U value, and performance.
WFM: Glass is the most common infill material used in curtain wall systems. What are the other cladding materials which can be used? What is the criteria for selection of cladding material including glass?
Ar Sandeep Shikre (SS): It is important to know the properties of glass before working with it. Glass is the most preferred material because of its transparency, strength, availability of colours and graphics which can be imposed on it, etc. It is a plane material and hence can be used against stone or any other cladding. It occupies less space, thus increasing the carpet area.
But the material could be ACP, solid metal sheets, honeycomb panels, laminates, clay tiles, vitrified tiles, zinc or stainless-steel cladding (Petronas towers), lightweight stone cladding or vitrified tiles. The architect’s design will define the transparent and opaque areas as per need.
Enquire Now for Aluminium Composite Panel (ACP)
ACP is not as durable as glass. The colour fades over a period of time and lifespan is less. If it is not of good quality, it discolours. In rainy seasons or when it is exposed to rains for a long time, it gets water marks. It is not a robust material as glass. We prefer going for a solid metal sheet rather than ACP. Zinc or other alloys or terracotta/ stone claddings /aluminium wall cladding or laminates are more robust.
WFM: Please brief on the key factors escalating the performance of façades?
Ar Sandeep Shikre (SS): Through computer simulation, we can actually put the building on a plot with similar weather chart and test for various aspects. We can exactly see the behaviour of the building in various seasons, and can actually do the sunpath analysis, etc. We can test with various envelope strategies and arrive at the optimal design. The façade model can be tested on energy simulation model,

Corporate HQ for Mudra DDB , Mumbai
sun path analysis and then, check the performance of the materials available like U value of glass which will cut down the heat gain. Performance of a façade is measurable and it is available to every architect/ developer to understand much before he commits for any particular façade design.
Analysing the life and fire safety of the building is another important aspect. Through the computer simulated analysis of designs, we can escalate performance of a building. One should not over design too to reach the optimal level.
WFM: According to you, what is the latest technology in curtain wall systems?
Ar Sandeep Shikre (SS): Latest technology is unitised system. Leather cuts in fabrication, highly sophisticated Aluminium extrusions are few state-of-the-art technologies available. Creative media walls is a revolutionary idea. Here, the façade speaks with the people, like the Kohinoor towers façade which communicates.Then there are motorised façades with automatic sensors. They create intelligent façades through computer automation. We also have façades with photo-voltaic cells to generate energy.






















Post A Comment