What Is An Electrical Wire?
An electrical wire is a single conductor made of material like aluminum or copper which are made up of electrically conductive material. These can also be a bundle of conductors encased in an insulating sheath. The main purpose of electrical wiring is to transmit electrical power or signals within a circuit or between devices. Wires can be solid, consisting of a single, rigid conductor ideal for fixed installations, or stranded, composed of multiple flexible strands twisted together for enhanced durability and flexibility.
Post your Requirement
Electrical wires are fundamental components in building wiring, enabling the distribution and control of electricity to appliances, lighting, and other electrical devices. Their selection and installation maintain safety, efficiency, and reliability in electrical systems. The insulation surrounding the conductors prevents unintended contact and ensures safe operation. Coloured sheathing identifies different wire functions such as neutral, ground, or live in electrical systems.
What Are Cables?
Cables consist of multiple insulated conductors or wires that are grouped. These are designed to transmit electrical or telecommunication signals from one transmitter to another safely and efficiently. These conductors can be twisted, bonded, or braided together within the cable structure. Cables provide more protection compared to individual wires as they shield against external interference and help to prevent electrical hazards.
Common types of cables include twisted pair, coaxial, multi-conductor, and fibre optic cables, each used with specific applications.
Difference Between Electrical Wire And Cable?
Electrical wires and cables are essential components in electrical and communication systems. Both electrical wire and cable are more often interchangeably used but have a huge difference. Each has its usage, type and advantages and depending on your need you can opt for any.
|
Aspects |
Wires |
Cables |
|
Definition |
Wires consist of a single conductor made from metal (like copper or aluminium) and are used for carrying electricity or signals over short distances. They can be solid or stranded. |
Cables are assemblies of two or more conductors, each with their insulation, grouped together and often surrounded by an outer protective jacket. |
|
Classification |
Wires are single conductors designed to transmit electrical signals or power. |
Cables have multiple conductors bundled together within a single structure. |
|
Uses |
They are versatile and used in various applications such as electrical wiring in buildings, transmitting signals in telecommunications, and even in non-electrical applications like jewellery and clothing. |
They are designed for specific purposes such as power transmission, high-quality audio and video transmission (like HDMI cables), and telecommunications. |
|
Types |
There are two main types of wires:
|
Cables come in several types:
|
|
Application |
Used in everyday applications such as household wiring, electronics, and telecommunications for short distances. |
Used in more complex scenarios requiring high durability and specific transmission characteristics, such as industrial machinery, underground installations, and high-performance audio/video systems. |
|
Advantages |
|
|
Terminologies Regarding Electrical Wiring
There are different terminologies we use every day which correlate to electrical wires. Having a better understanding of each of these terms will give you an upper hand in choosing the right kind of wiring for your needs.
1. Wire label: There are many wires used in residential settings but the most common type includes a nylon-coated thermoplastic that offers high heat resistance. These electrical wires are labeled as THHN/THWN which stands for;
- T – Thermoplastic insulation
- H – Heat resistant
- HH – High heat resistance generally up to 194 degrees Fahrenheit
- W – Rated for wet locations
- N – Nylon-coated which helps to resist damage from gasoline
- X – Synthetic polymer, flame-resistant
Along with this, there is also the mention of material, maximum voltage rating and gauge. Generally, the THHN material wires are made for 75 degree Celsius temperature and THWN can usually handle higher degrees.
2. Wire Material: The most common type of conductor for residential electricity is copper. Most wires are marked with CU which stands for copper. These wires are properly insulated as electricity travels on the outside of copper. Proper insulation ensures protection against fire and shock.
Aluminum wires offer an alternative to copper wire but degrade fast. These wires are more conductive but because of low durability are not used in residential settings. Aluminum wires are generally installed only by professional electricians and they have to comply with NEC guidelines.
3. Maximum Voltage Rating: There is a number written on the wire, usually 600 which indicates the maximum voltage the wire can carry. The average household voltage is usually around 120 to 240 volts. There is a formula you can apply to calculate the maximum wattage any wire or cable can hold which is
Amperage x voltage = watts
Here, amperage is the strength of an electric current. Voltage stands for electrical force needed to drive current between two points and wattage refers to the amount of electricity used.
4. Wire Colours: The purpose of different wire colours is to differentiate between different purposes for wires. We should always test the wires with a volt checker as neutral can be as dangerous as a hot wire. Let’s look at the different colours and their purpose as provided by NEC reference-
- White insulation: Indicates neutral wire but can sometimes also be as hot lead.
- Green insulation: Ground wire.
- Blue or yellow insulation: Got wire pulled through a conduit.
- Black insulation: Hotwire for switches and outlets.
- Red insulation: Hotwire for hardwired smoke detectors and switch legs.
5. Gauge: As defined by the American wire system, The wire gauge refers to the electrical wire sizing. The diameter and the gauge of any wire are inversely related meaning as the gauge size gets lower, the diameter gets bigger. The most common gauges are numbered 10, 12 and 14. If your construction needs require you to opt for a longer length of wire, always increase the gauge size too as it will ensure that the electricity passes through smoothly.
6. Cable labelLing: Cables are labelled and printed to provide you with all the information such as type, gauge, underwriter laboratories, number of wires, grounding, and voltage rating. This helps you to decide which cable will be appropriate for your project.
Types Of Electrical Wire
There are several types of wires used by electrical contractors for different purposes and applications in the electrical systems of buildings. Some of the widely used types are discussed below;
1. NM-B Cable:
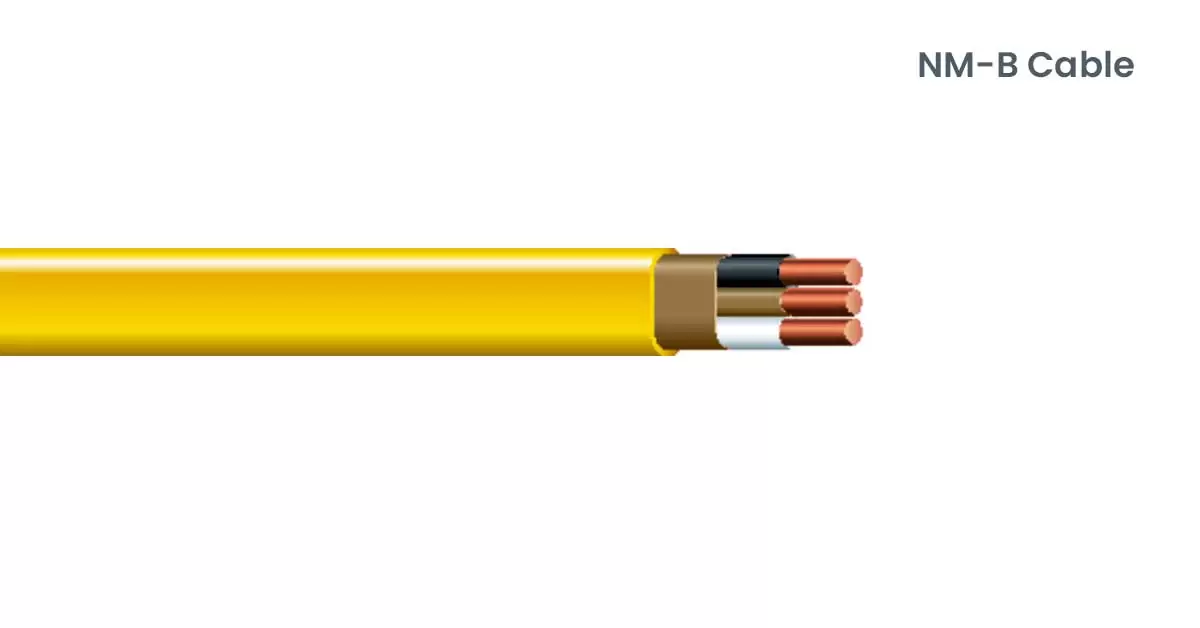

Non-metallic (NM) cable, commonly known by the brand name “Romex,” is a widely used type of electrical wiring designed for interior applications in residential buildings. The name “NM” denotes its non-metallic sheathing, typically made of thermoplastic material, which encloses two or more insulated wires of the same gauge. This sheathing protects against mechanical damage and electrical insulation.
NM cable is most suitable for dry environments indoors, such as behind walls, in ceilings, and within floor cavities, where it is protected from moisture and excessive heat sources. It is not intended for outdoor use or direct burial.
Inside the NM cable sheath, there are insulated conductors coloured white for neutral, black for hot, and sometimes bare copper for ground. These wires facilitate safe and efficient electricity transmission within the building. The “B” designation in NM-B cable signifies its heat resistance rating of up to 194 degrees Fahrenheit, ensuring safe operation under normal household electrical loads.
2. UF Cable:
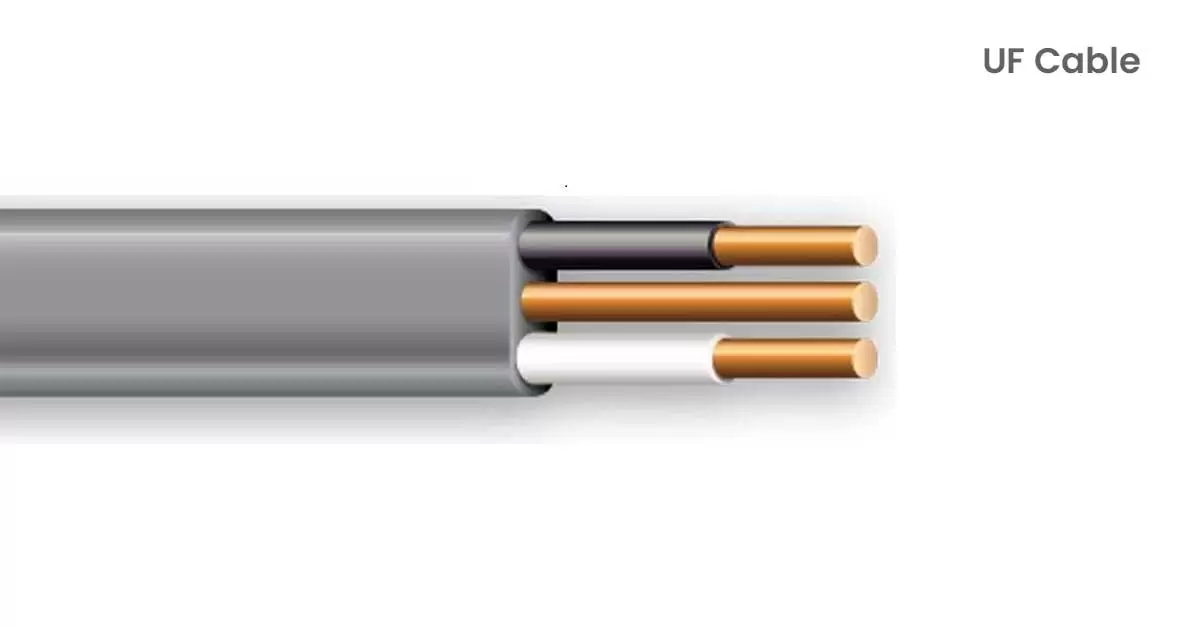
Underground Feeder (UF) cable is specifically designed for outdoor and underground installations where it will be exposed to moisture and soil but can withstand it. It resembles NM cable but has a tougher, solid plastic sheathing that encases all of its wires together. Its strong build protects the insulated hot, neutral, and ground wires from environmental elements, ensuring reliable electrical connections in harsh conditions.
UF cable is commonly used to power outdoor fixtures like lampposts, garden lights, and garage outlets. Its durability comes at a slightly higher cost compared to NM cable due to the thicker insulation required for outdoor use. UF cable is typically identified by its grey outer sheathing.
When installing UF cable, it’s crucial to bury it at an adequate depth to shield it from physical damage and to follow local building codes. If a UF cable needs to be exposed above ground or in areas prone to mechanical impact, it should be protected by a conduit.
3. Armored Cable:
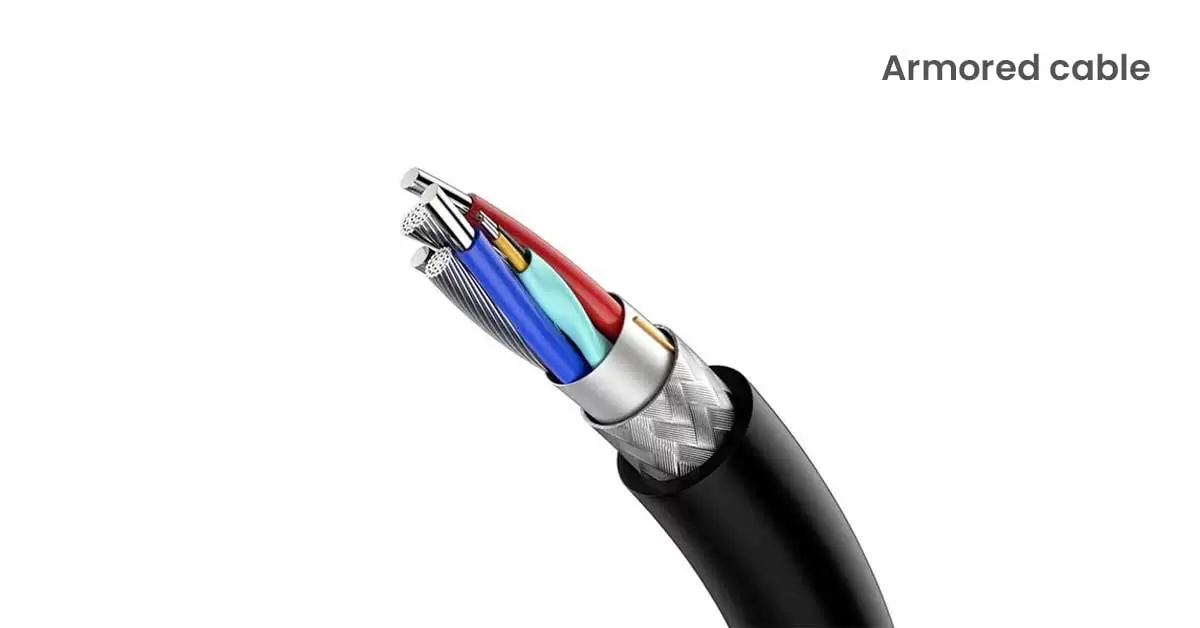

Armored cable, also known as BX cable, is a type of wiring that includes insulated hot and neutral wires along with a bare bonding wire, all encased in a protective metal sheathing. This metal sheath serves 2 purposes, the first being it shields the internal wires from physical damage and acts as the grounding conductor for the electrical system.
These are typically found in older homes and are primarily used indoors where they provide robust protection against impact, cutting, and even rodent interference. It’s commonly used in commercial and industrial settings as well, where durability is crucial. While armoured cable eliminates the need for additional conduits, it is relatively expensive and can be challenging to install due to its weight and rigidity.
4. Metal Clad Cable:
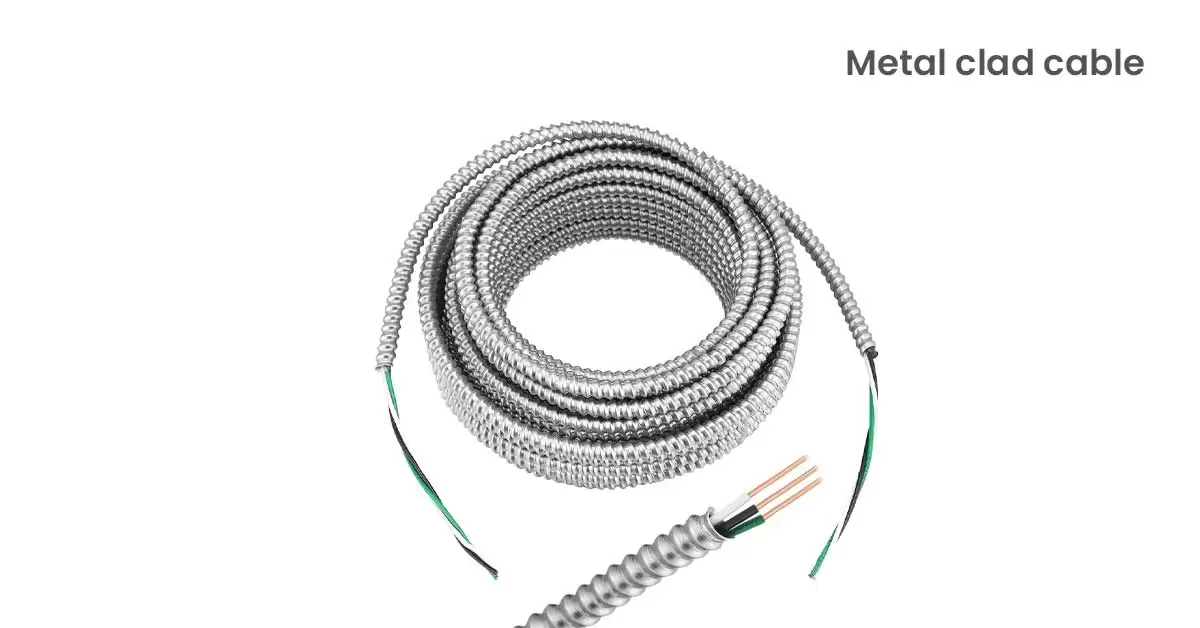

Metal-clad cables are somewhat similar to AC but are wrapped using plastic instead of paper. It features a protective metal sheathing that shields the internal wires, ensuring durability and protection against physical damage. MC cable is primarily intended for indoor use and is less commonly used in residential applications compared to AC.
MC cable has a green grounding wire because its metal sheathing cannot be used as a ground. The lighter aluminum or steel armour of MC cable enhances its flexibility, making it easier to install in various settings, including commercial and industrial environments.
5. THHN/THWN Wire:
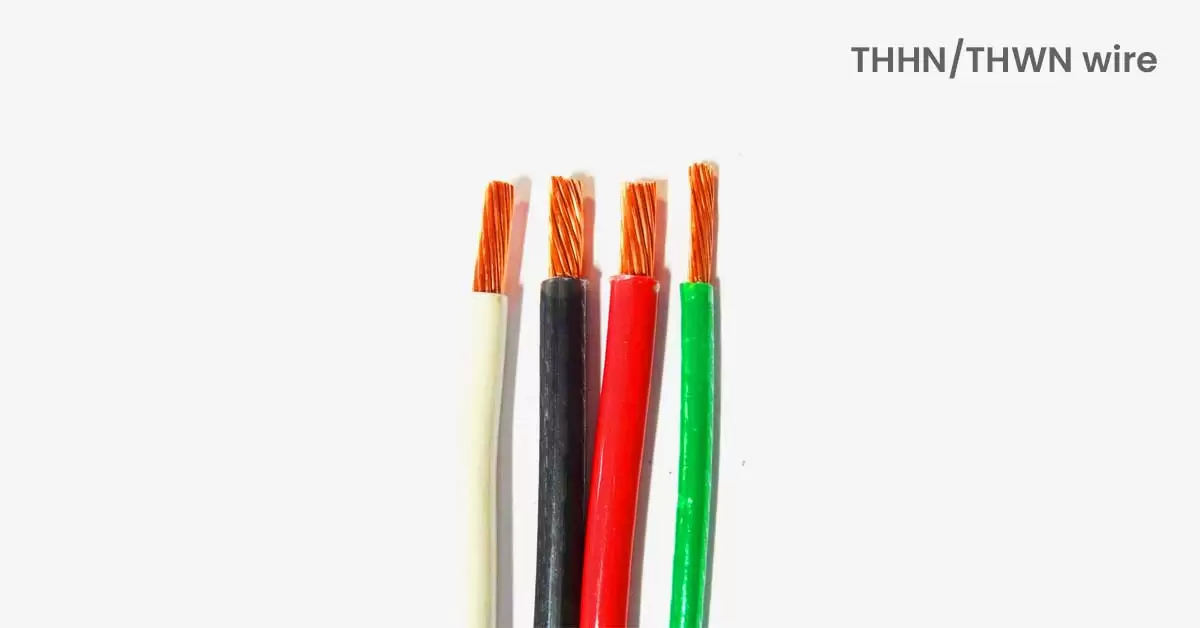

Thermoplastic High Heat-resistant Nylon-coated and Thermoplastic Heat and Water-resistant Nylon-coated are two types of insulated electrical wires commonly used inside conduits. Unlike NM cables which bundle multiple insulated conductors in plastic sheathing, THHN and THWN wires are single conductors with their color-coded insulation. Instead of being protected by NM cable sheathing, these wires are shielded by tubular metal or plastic conduit.
Conduit is typically used in unfinished areas like basements and garages, and for short exposed runs indoors, such as wiring for garbage disposers and water heaters. These wires are generally priced similarly to NM wire plus the cost of conduit.
These wires are durable and suitable for various applications, offering resistance to heat and moisture depending on the type. Proper installation in conduits or raceways is crucial, especially in exposed or damp environments, to prevent damage and ensure safety.
6. Low Voltage Wire:
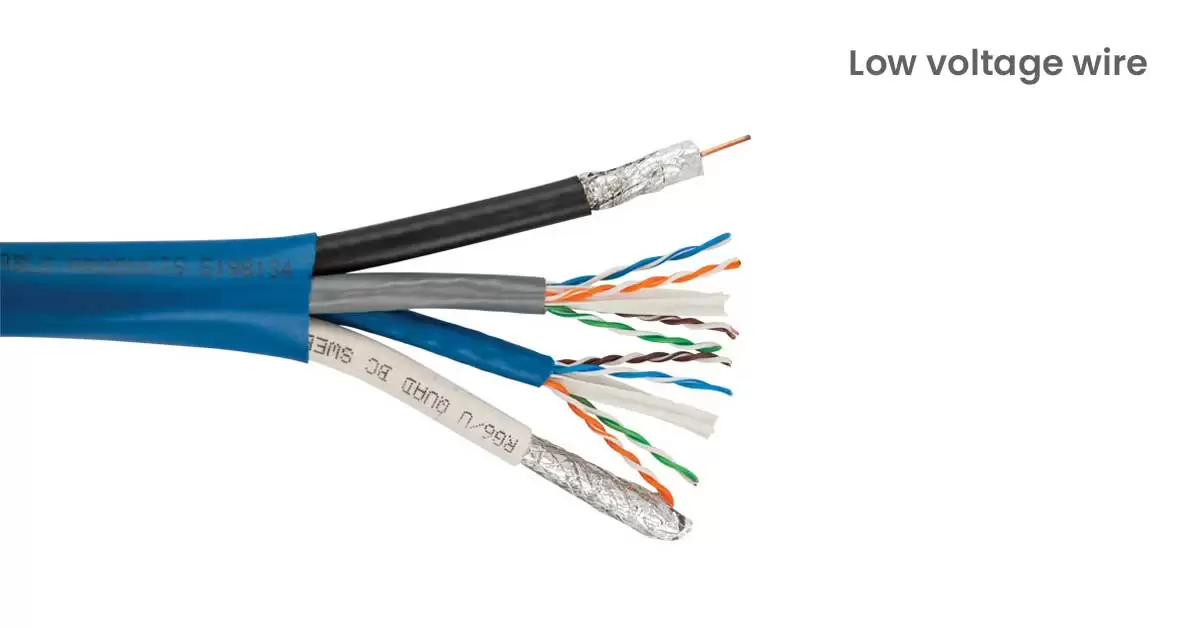
Low-voltage wiring also known as low-tension cable is used for that operate at 50 volts or less, like landscape lighting, doorbells, and thermostats. These wires are typically made of copper or aluminum and range from thin 22-gauge to thicker 12-gauge sizes. They are often insulated and can be bundled in cable sheathing or twisted pairs.
Low-voltage wires are safer than standard electrical wires, reducing the risk of shocks and fires, which makes them great for DIY projects. When installing low-voltage wiring, plan carefully to avoid interference with high-voltage lines and ensure good performance.
7. Coaxial Cable:
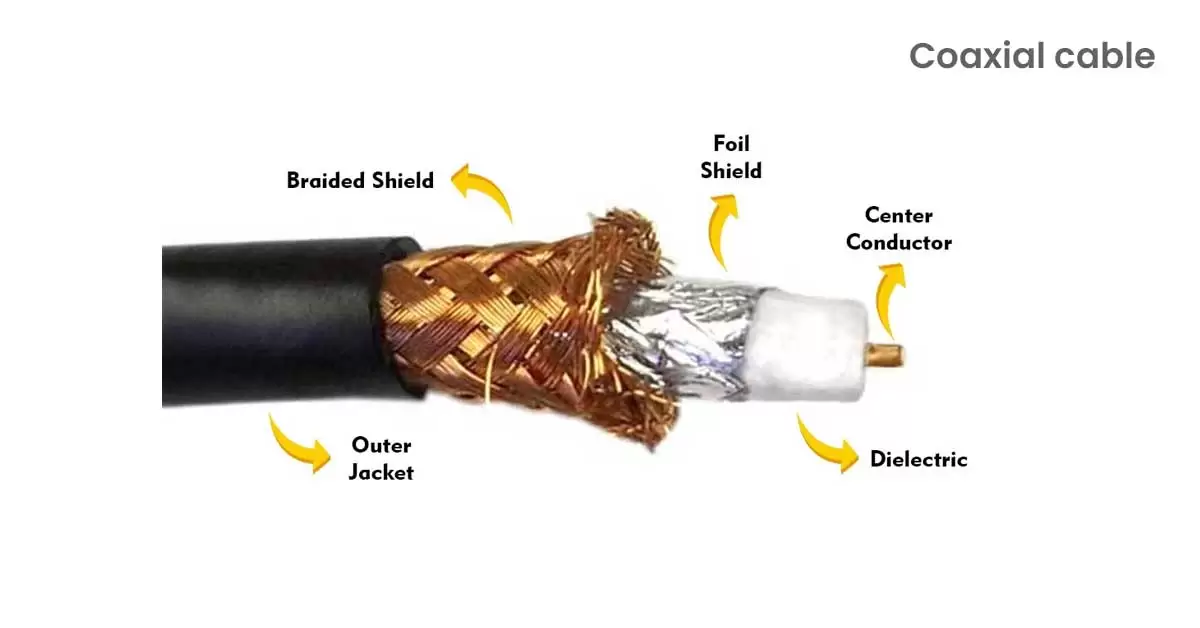
Coaxial cables, commonly known as coax, are important for TV and internet connections in homes and businesses. It consists of a central wire conductor, surrounded by a non-conductive insulating layer, a metal shield, and an outer protective layer. This design prevents electromagnetic interference, ensuring high-quality transmission of video and broadband signals over long distances.
There are different types of coaxial cables like RG6 and RG11. RG6 is widely used indoors for cable TV and internet due to its balance of performance and flexibility. RG11 is thicker and less flexible, suitable for outdoor or longer-distance installations where signal loss needs minimizing. To optimize signal quality, use the shortest coaxial cable possible between your service provider’s entry point and your devices. Use high-quality cables and connectors to avoid performance issues.
8. Instrumentation Cables:
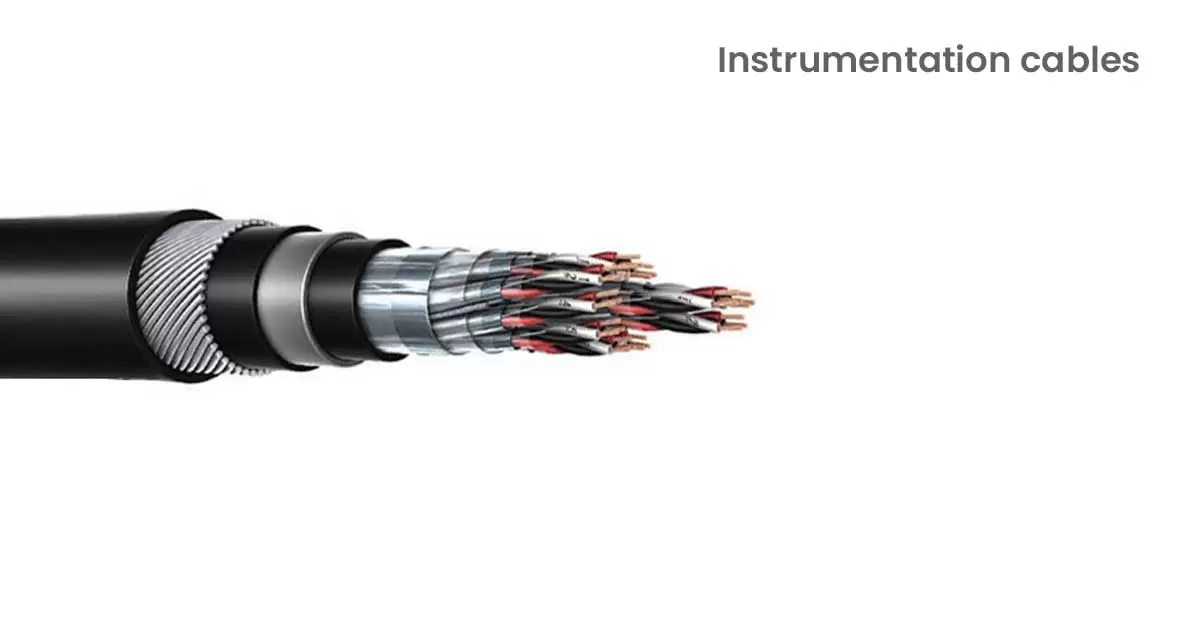

Instrumentation cables are tough and strong cables used on construction sites and in wired networks to connect operators with instruments. They carry low-energy electrical signals effectively due to their multiple copper conductors. These cables are mainly used in industries because they are durable and sturdy.
Instrumentation cables have layers like PE bedding, galvanized steel wire, outer and inner sheaths, PVC coatings, and sometimes copper wire braiding. These layers protect the conductors from moisture, rust, chemicals, oils, and solvents.
9. Ethernet Cable:
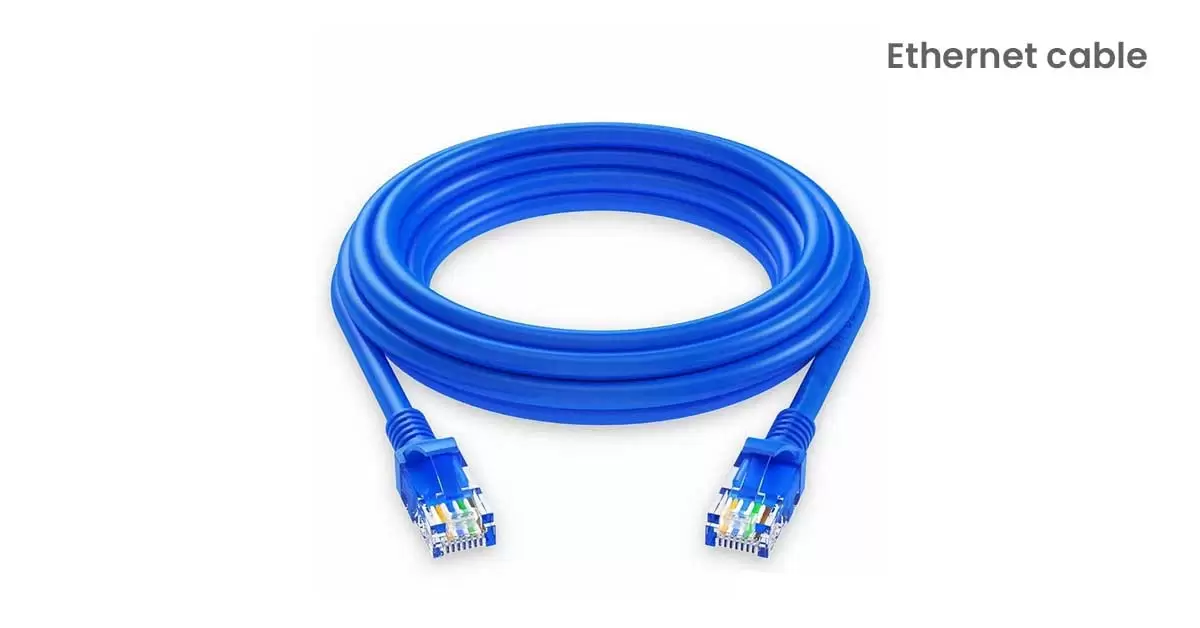

An Ethernet cable is used in wired networks to connect devices like PCs, routers, and switches within a local area network. These cables come in a variety of length and quality which affect their ability to transmit a strong network signal. Different types of Ethernet cables are designed for specific tasks and conditions to optimize performance.
Physically, an Ethernet cable looks like a larger version of a traditional phone cable but with eight wires instead of four. Both have similar plugs and shapes, but Ethernet cables are larger overall. These cables are essential for reliable network connections in homes, offices, and other settings.
10. Category 5e Cable:
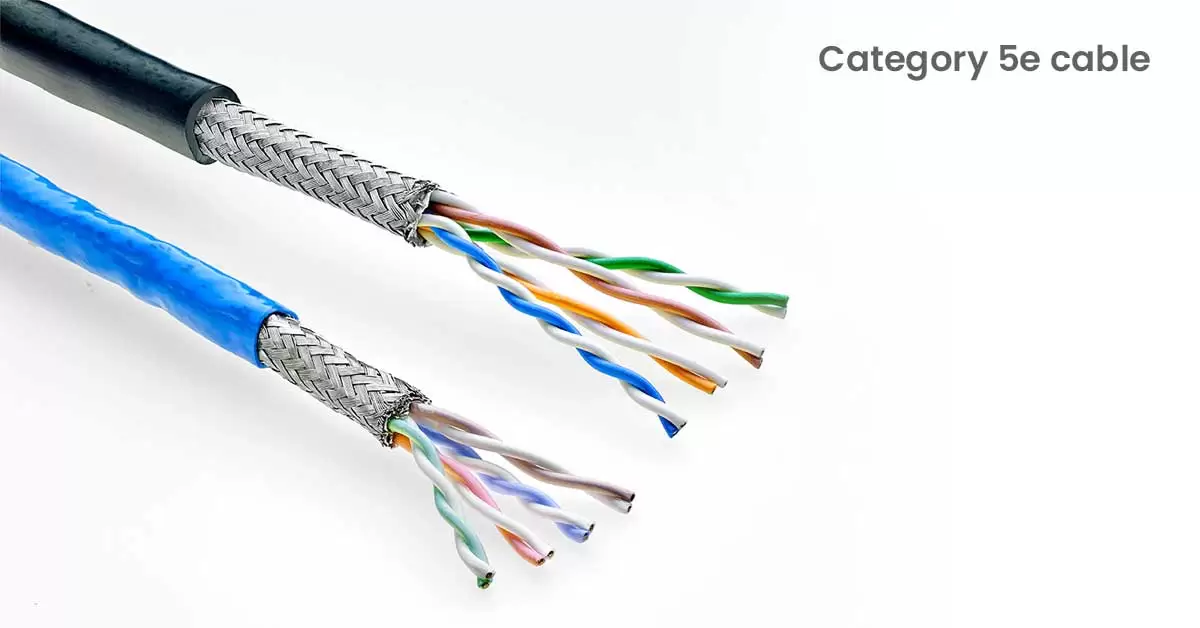

Category 5e cables are often known as Cat-5e or Ethernet cables. These are the standard choice for unshielded twisted-pair (UTP) connections. It’s used widely to link phones, computers, home automation systems, and audio/visual networks. This type of cable typically includes 4 pairs of wires (totalling 8 conductors) encased in one protective jacket made of copper. These are the most popular types of telephone cable.
11. Lamp Wire:
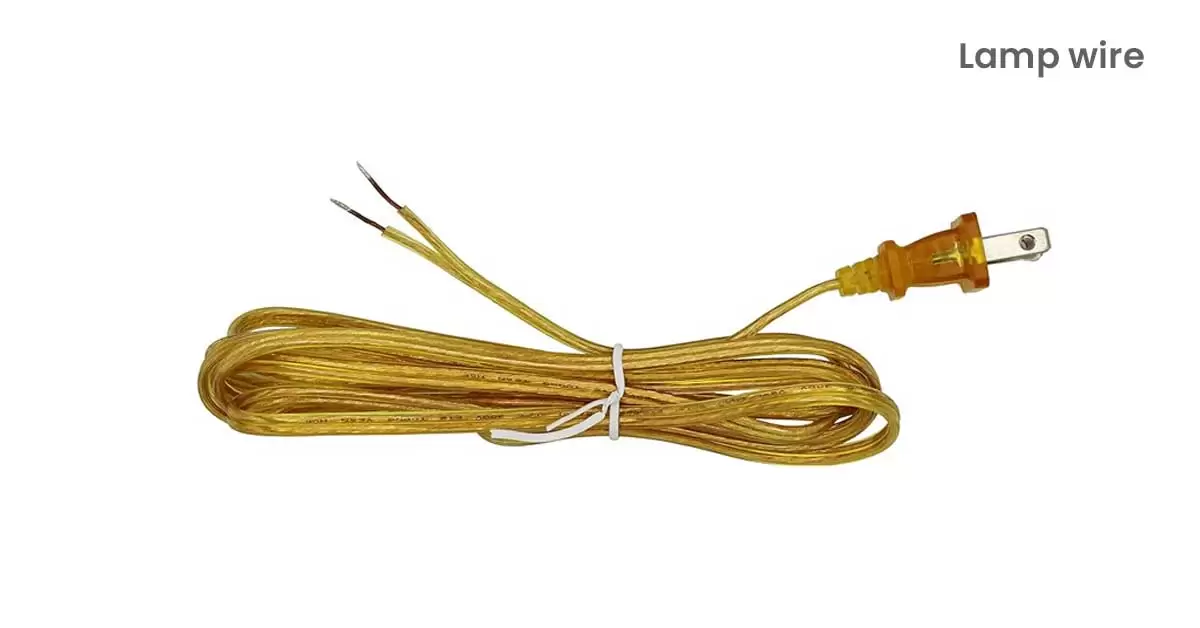

Lamp wire, such as SPT-1 and SPT-2, is designed for small household devices like lamps, clocks, and fans. It’s not meant for heavy-duty applications and can withstand temperatures up to 105 degrees Celsius.
12. Landscape Cable:
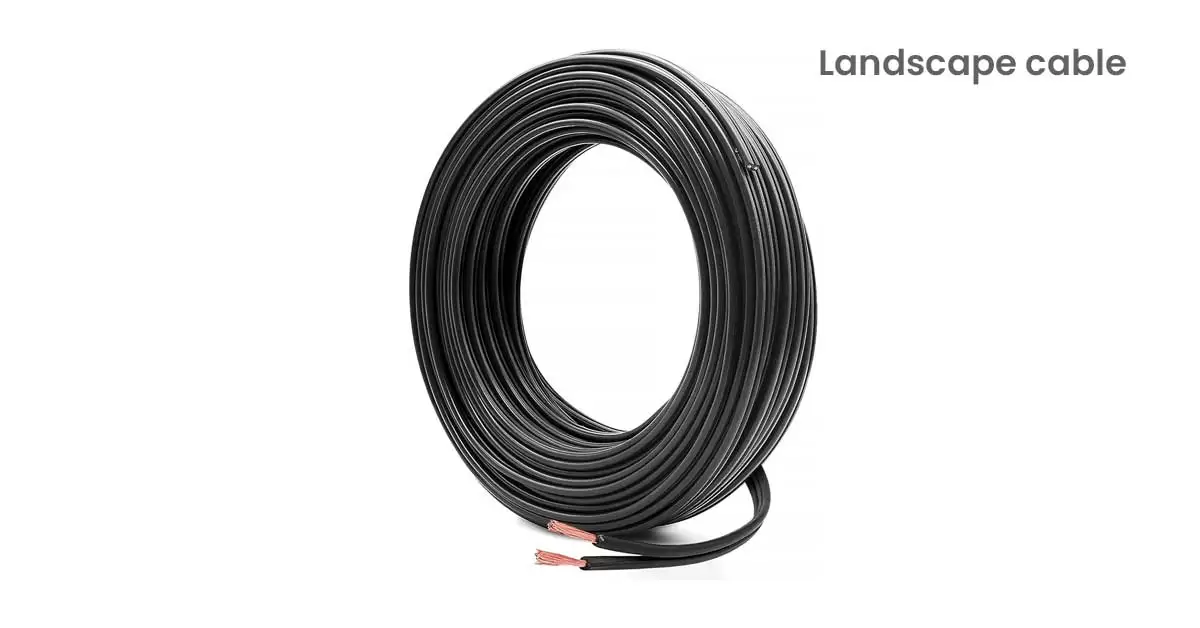

Landscape cable is suitable for low-voltage underground use and is ideal for outdoor security lighting and accent lighting. It should not exceed 150 volts as per the National Electrical Code (NEC) and other standards. This cable is resistant to sunlight and UV rays, making it safe for direct burial. It operates effectively in temperatures ranging from -20 to 60 degrees Celsius and is equipped with copper conductors for reliable performance.
13. High Tension Cable:
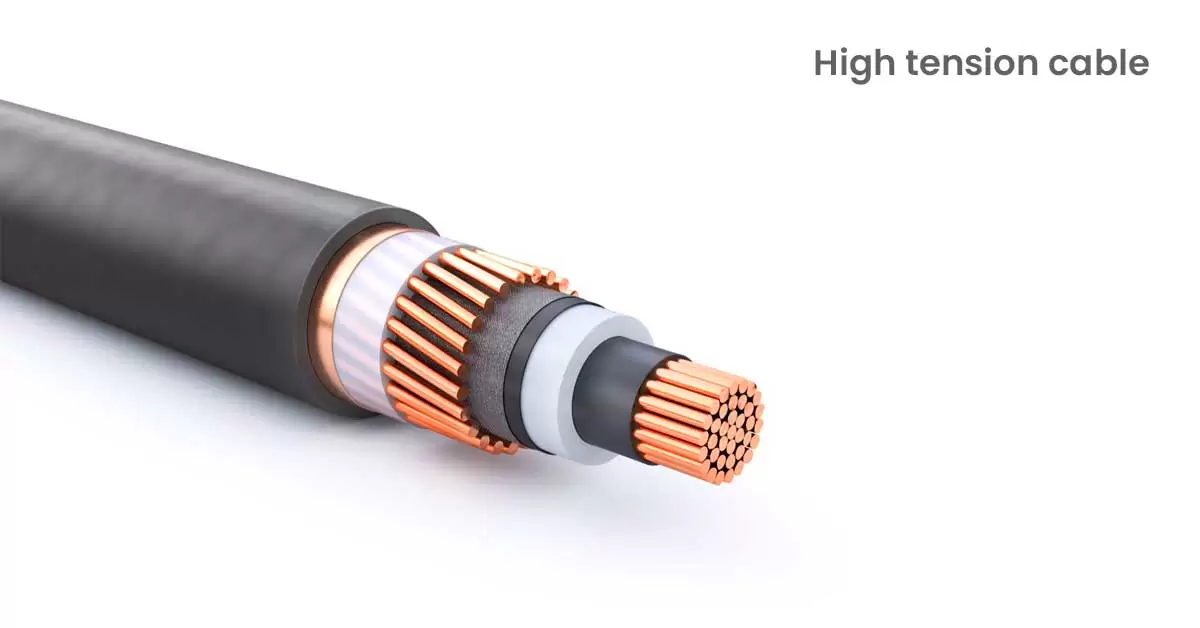

High-tension cables are used when you require voltage levels up to 11 kilowatts. They are specially designed to transmit high-voltage power without overheating or causing electrical fires. These wires are highly insulated which prevents electrical shocks during installation and maintenance. HT cables are used for transmitting electricity or when underground transmission is required.
These cables are often laid in ducts or buried deep in the ground and are made of superior-quality aluminium. They are widely used for underground power distribution, industrial applications and offshore applications.
Metals Used For Making Electrical Wiring
There are several types of metals that we use in electrical wiring and cable for both commercial and residential settings. They are as follows;
- Copper- The most commonly used type of metal for making wiring and cable is copper. It is a highly conductive metal which allows electricity to pass through it easily. It is relatively inexpensive than the other metals being used like gold which is the highest conductive metal. This makes copper the best conductor of electricity which is also economical and affordable. Copper has a distinct feature in that it is ductile meaning it can blend, fold and flex to any degree without causing any damage to the insulation and wire. Additionally, another benefit of copper is its property of being thermal resistant which enables it to withstand large amounts of heat and helps prevent fire. Lastly copper is also a recyclable material making it a green choice.
- Aluminum- Due to its extensive availability and low cost,aluminum is also used for making wires and cables. It is a great conductor of electricity and has been used for more than 100 years. Aluminium is both durable and ductile making it flexible to be bent and molded. Wires made from aluminum are also lightweight making it the preferred choice for high-voltage lines. These are durable and corrosion-resistant making their lifespan more than that of silver and gold. Aluminum offers two times the conduct per pound of wiring made of copper. It is also a thermal resistant material which makes it best for industrial and residential buildings.
- Tungsten- Also called wolfram is a less common metal used for wiring. This metal is strong and highly durable against heat and wear because of refractory metal. Tungsten is often alloyed with steel which increases its strength and hardness. It is an expensive option used for centuries in wiring as filaments for lighting, electron tubes and electrodes.
- Gold- The not-so-commonly used material for making wire and cable is gold. Gold is highly conductive and provides a superior level of electricity conductivity when compared to copper, silver and aluminum. The most commonly used type of gold wire is the thin wire or copper coated with gold on the connection point. This metal does not reach under normal conditions and is exceptionally solderable. This noble metal has excellent corrosion resistance and provides resistance to chemical attacks during high temperatures. It is always alloyed with nickel or cobalt making it more durable and flexible. It is used in home wiring because of its longevity and efficiency. The only disadvantage of using gold is its price.
- Silver- This oxidised metal is the most conductive metal used in electrical wiring. Silver provides you durability and flexibility which allows bending and flexes to mold the wire according to need. The downside of using silver is that it is expensive and it reacts to oxidation when exposed to the environment. Silver also has a higher rate of degradation than other materials being used and is a poor choice if you are looking for an affordable option.
Tips To Choose The Right Electrical Wiring
Choosing the right type of wiring for your houses or commercial property is necessary to ensure longevity and prevent hazards like fire and shocks. There are a lot of factors which you should consider before like intended purpose, insulation type, wire size, etc.
- Determine the Electrical Load- The first thing you need to do is calculate the electrical load or the total amount of power consumption through each circuit. For this, you must consider the number of appliances being used, their voltage, outlets and lighting fixtures that are connected to the main circuit. This process helps you find out the amperage or the capacity you will require for your estate wire.
- Select The Insulation Type- There are different insulations present in the market which are used for different purposes. For example, thermoplastic is used for indoor and dry locations, Thermoset is used for indoor and outdoor use and it provides better resistance to heat and moisture Underground-rated are designed for direct burial or underground installations and have moisture-resistant insulation.
- Intended Use- You have to decide which type of wire will suit your needs the best. Always select a wire based on the purpose you intend to use it for. For example, use low tension cable for low voltage use and high tension cable for electricity towers.
- Check Local Electrical Codes- Read and understand the local electrical codes. These rules outline the smallest size for house wires, the type of insulation needed, how grounding should be done, and the right ways to install everything. They’re there to keep things safe and make sure everything meets the right standards. If you’re unsure, get advice from your local building department or talk to a licensed electrician.
- Determine The Wire Size- To choose the right wire size, consider the circuit’s amp rating and how far the wire needs to run. You can find guidelines in the National Electrical Code (NEC) or ask an electrician for advice. Wire size is typically measured in American Wire Gauge (AWG), where higher numbers mean smaller diameters.
Safety Precautions To Be Followed While Installation
Installation of wiring and cables is a difficult task and must be carried out only by professional electricians as they make sure of installation codes and follow all the rules and regulations. The following things should be kept in mind during the installation process
- Proper Installation Techniques- It’s really important to install electrical wiring and cables correctly. If they’re not installed right, it can cause problems like inefficiency or even dangerous electrical fires. Always follow the instructions from the manufacturer and obey local building codes and the National Electrical Code (NEC). If you’re not sure, it’s wise to ask a licensed electrician for help to make sure everything is safe and done correctly.
- Protection From Physical Damage- Electrical wires and cables need to be shielded from physical harm during installation and while they’re being used. This means using protective tubes or strong coverings when needed. Also, make sure wires aren’t squeezed, twisted, or put under too much pressure. They should also be kept away from chemicals or extreme heat or cold that could damage them.
- Regular Maintenance and Inspection- To keep your electrical system safe and working well, it’s a good idea to check it regularly and do any needed maintenance. This includes looking for and fixing any worn-out insulation, loose connections, or signs of damage. Regular maintenance helps stop problems before they become serious, keeping your electrical system in good shape.
- Grounding and Bonding- Grounding and bonding are crucial for safety. Grounding gives electricity a safe way to go into the ground if something goes wrong, preventing shocks and fires. Bonding connects metal parts so electricity flows smoothly. Both of these are very important for keeping your electrical system safe.
Conclusion
Thus, knowledge about different types of wiring can help you choose the right one for all your needs. Many installation codes have to be followed, so it is a wise decision to hire a professional electrician or an electrical contractor. The right wiring can help you ensure your home’s power supply operates at peak efficiency with safety.
Read Also: An Ultimate Guide To Electrical Contractor: What Do They Do?
FAQ’S
Q:1 What is the most common wire used in houses?
A:1 The most common type of wire in houses is the non-metallic (NM) cable, also known as Romex cable. The NM cable refers to a flexible kind of cable that comprises multiple conductors including a ground wire and a neutral wire. These kinds of wires are widely used in homes for outlets, switches, appliances, and diverse other applications.
Q:2 Which wire is used for AC connection?
A:2 Copper wires with high-grade insulation capabilities are often the widely used kind of wires for AC connection. The size of the wires depends on the capacity of the air conditioner. The most common sizes of the wires are 10 AWG, 8 AWG, or 6 AWG, depending on the AC unit’s power rating.
Q:3 Which type of wire is best for house wiring?
A:3 Copper wires with PVC insulation are considered to be the best for house wiring due to their high conductivity, flexibility, and durability. The preferred types often include FRLS (Flame Retardant Low Smoke) wires for safety against fire, XLPE-insulated wires for better heat resistance, and multi-strand copper wires for better flexibility and durability.
Q:4 Which type of cable is best for outdoor use?
A:4 The Underground Feeder (UF) cable and Armored Cable (AC or BX cable) are some of the best options for outdoor applications. The UF cables are effectively moisture resistant and can also be used directly underground while the armored cables with the ability to ensure additional protection in exposed environments.
Q:5 What are the color codes for electrical wiring?
A:5 The electrical wiring color codes in India follow the IEC (International Electrotechnical Commission) standard. The standard color codes used in India can be defined as follows:
Single-Phase Wiring:
- Live (Phase): Red or Brown
- Neutral: Black or Blue
- Earth (Ground): Green or Green-Yellow
Three-Phase Wiring:
- Phase 1 (L1): Red
- Phase 2 (L2): Yellow
- Phase 3 (L3): Blue
- Neutral: Black
- Earth (Ground): Green or Green-Yellow























Post A Comment